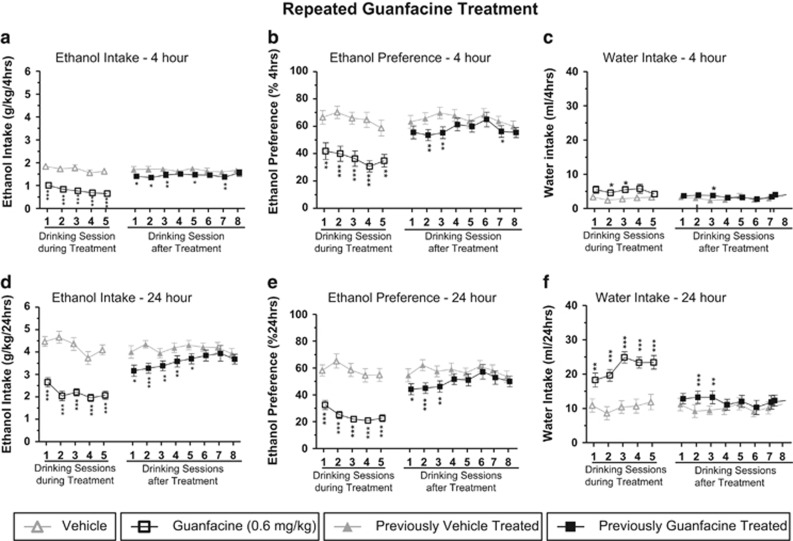
Figure 2.
Repeated guanfacine treatment (0.6 mg/kg/day over 5 consecutive alcohol drinking sessions) significantly decreased voluntary alcohol intake ((a) 4 h time point and (d) 24 h time point) and preference for alcohol ((b) 4 h time point and (e) 24 h time point) compared with vehicle in rats that had been consuming high amounts of alcohol (4.3±0.2 g/kg per 24 h) for ∼7 months before the treatment. There was no tolerance development during treatment and the significant decrease persisted for up to five drinking sessions after the last injection. In addition, there was a significant increase in the water intake ((c) 4 h time point and (f) 24 h time point) compared with vehicle. All values are expressed as mean±SEM; n=12; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with corresponding vehicle (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by planned comparisons).