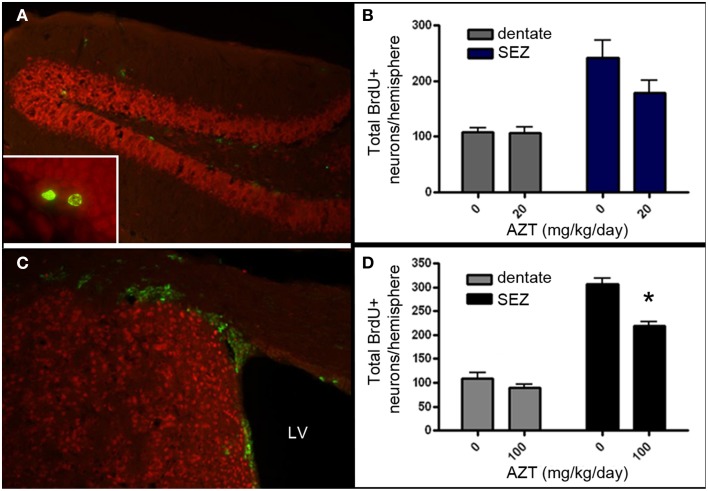
Figure 7.
AZT reduces SEZ but not hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo. Adult mice received a 2-week regimen of AZT (20 or 100 mg/kg/day, i.p.). On the day after the last AZT injection, animals received 4 successive injections of BrdU (100mg/kg) at 2-h intervals. One week later the animals were euthanized and the brains were processed and analyzed. Representative epifluorescence images of coronal sections through the hippocampal dentate gyrus (A) and SEZ (C) of the adult mouse immunolabeled for BrdU (green) and NeuN (red). Inset in (A) shows two BrdU+ (green) cells in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus, immediately superficial to the subgranular zone.Neither the 20 mg/kg/day (B) nor the 100 mg/kg/day (D) regimen significantly altered the number of newly-generated cells (green) in the dentate gyrus (gray bars in both B,D). However, both regimens reduced proliferation in the SEZ (blue bars in B, black bars in D), though only the 100 mg/kg AZT dose reached statistical significance. Unpaired Student's t-test. NS, no significant difference. Asterisk indicates significant difference, p < 0.01. N = 4 for all groups. Error bars represent standard deviation.