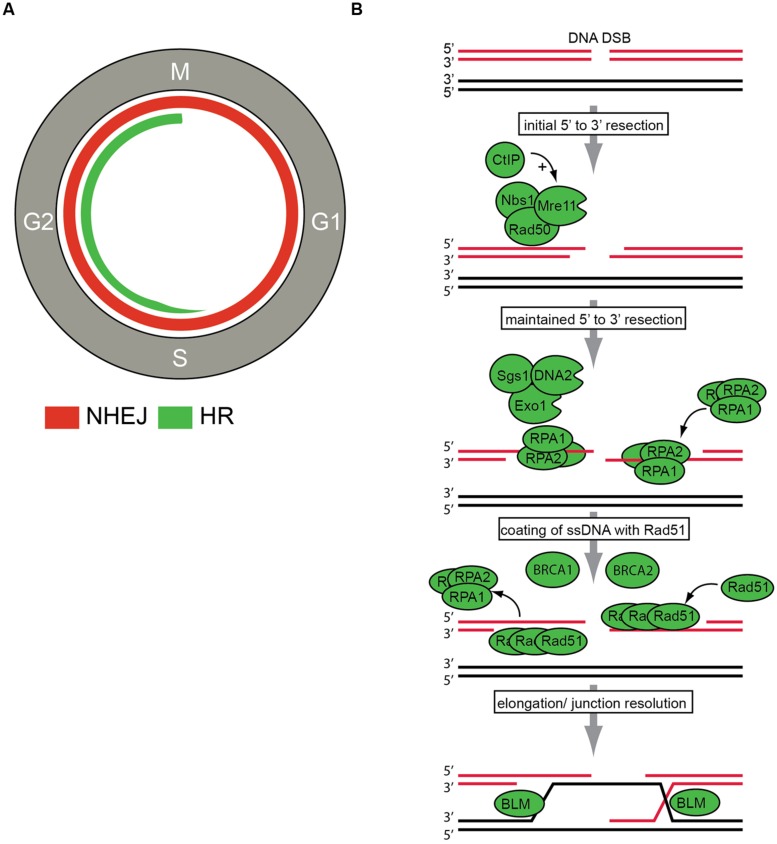
FIGURE 1.
DNA double strand break (DSBs) repair. (A) DNA DSBs repair pathways in the context of cell cycle regulation. Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) can be performed throughout the cell cycle and is indicated with the red line. Homologous recombination (HR) can only be employed in S/G2 phases of the cell cycle and is indicated in green. (B) The key steps in HR repair pathway are indicated. After DSB recognition, 5′–3′ end resection is initiated by the MRN (Mre11, Rad50, Nbs1) complex and CtIP. Subsequently, further resection by the Exo1, DNA2, and Sgs1 proteins is conducted to ensure ‘maintained’ resection. Then, resected DNA-ends are bound by replication protein A (RPA). The actual recombination step within HR repair, termed strand exchange, is executed by the recombinase Rad51. Rad51 replaces RPA to eventually assemble helical nucleoprotein filaments called ‘presynaptic filaments.’ This process is facilitated by other HR components, including BRCA1 and BRCA2. Final step of junction resolution is executed by helicases including Bloom syndrome, RecQ helicase-like (BLM) helicase.