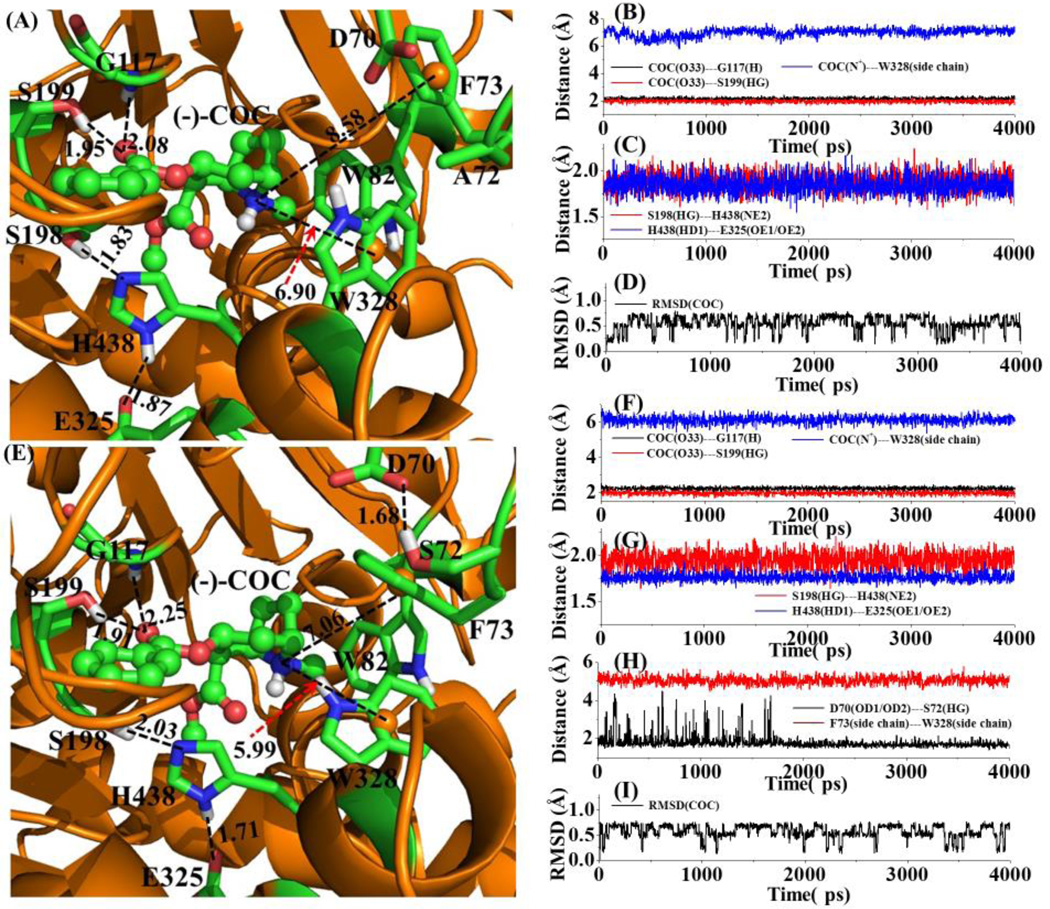
Figure 5.
The MD-simulated structures of mCocH and hCocH binding with (−)-cocaine: (A) mCocH-(−)-cocaine binding structure; (B) and (C) plots of key distances in the mCocH-(−)-cocaine complex versus the simulation time; (D) plot of root-mean-squares deviation (RMSD) of the atomic positions of (−)-cocaine in the mCocH-(−)-cocaine complex versus the simulation time; (E) hCocH-(−)-cocaine binding structure; (F) to (H) plots of key distances in the hCocH-(−)-cocaine complex versus the simulation time; (I) plot of the RMSD of the atomic positions of (−)-cocaine in the hCocH-(−)-cocaine complex versus the simulation time. COC refers to (−)-cocaine. COC(O33)---G117(H) represents the distance between the carbonyl oxygen on the benzoyl group of (−)-cocaine and the backbone hydrogen atom of G117; COC(O33)---S199(HG) the distance between the carbonyl oxygen on the benzoyl group of (−)-cocaine and the hydroxyl hydrogen of S199 side chain; COC(N+)---W328(side chain) the distance between the positively charged nitrogen of (−)-cocaine and the center of aromatic side chain of W328; S198(HG)---H438(NE2) the distance between the hydroxyl hydrogen of S199 side chain and the nitrogen atom (NE2) of H438 side chain; H438(HD1)---E325(OE1/OE2) the distance between the hydrogen atom (HD1) on the nitrogen atom of H438 side chain; COC(C32)---S198(OG) the distance between the carbonyl carbon on the benzoyl group of (−)-cocaine and the hydroxyl oxygen of S198 side chain; D70(OD1/OD2)---S72(HG) the shortest distance between the oxygen atoms of D70 side chain and the hydroxyl hydrogen of S72 side chain; and F73(side chain)---W328(side chain) the distance between the positively charged N atom of (−)-cocaine and the center of aromatic ring of W328 side chain. All distances and RMSD are given in Å.