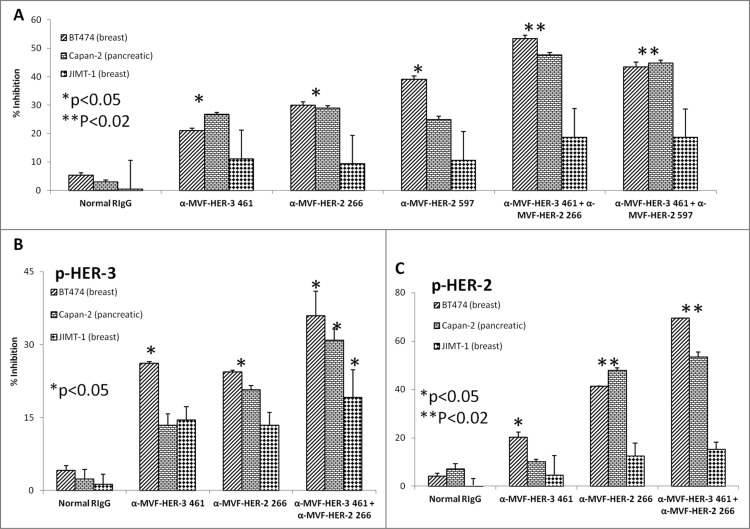
Figure 10.
HER-3 vaccine antibodies produce synergistic antitumor effects when used in combination with HER-2 vaccine antibodies. Cancer cells (BT474, Capan-2 and JIMT-1) were seeded and treated for 1 h with either HER-3 461 vaccine antibodies, HER-2 266 vaccine antibodies, HER-2 597 vaccine antibodies or a combination of antibodies prior to ligand stimulation with HRG (50 ng/mL). After 72 h of incubation in the presence of the inhibitors, cells were analyzed for proliferation via MTT inhibition assay (A). Percent inhibition was calculated by taking absorbance (abs) readings at 570 nm and using the following equation: (abs. untreated-abs. treated)/abs. untreated × 100. Cells were also seeded and treated with the various combinations of vaccine antibodies for 1 h prior to ligand stimulation (HRG) and cell lysis. Cell lysates were used to measure inhibition of phosphorylation of both HER-3 (B) and HER-2 (C) via ELISA kits from R+D Systems. Percent inhibition was calculated by taking the absorbance at 450 nm and using the same equation mentioned above (in A). In all experiments, normal rabbit IgG (Pierce) was used as a negative control. Results display averages of two independent experiments with triplicate samples (n = 3). Error bars represent SD of the average. Combination treatment showed a better significant effect in both the proliferation and phosphorylation assays (**p < 0.02 in both proliferation and HER-2 phosphorylation assays with the BT-474 breast and Capan-2 pancreatic cancer cells) while single treatment with the HER-3 or HER-2 inhibitors showed a lesser significant value (*p < 0.05) or was not significant.