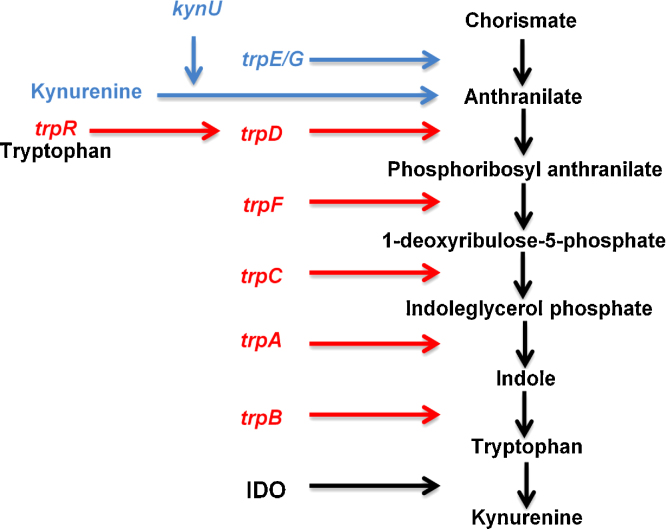
Fig. 1.
The tryptophan biosynthetic pathway. Tryptophan is synthesised from chorismate and kynurenine via anthranilate. The chorismate to anthranilate step is mediated by trpE/G (genes are present in Escherichia coli but not present in Chlamydia spp.) whereas the kynurenine to anthranilate step is mediated by host kynurinase. Chlamydia pecorum and Chlamydia caviae encode an almost complete tryptophan biosynthesis operon that includes the tryptophan repressor (trpRDCFBA) and is switched on when intracellular tryptophan levels decrease. Chlamydia abortus and Chlamydia muridarum lack all of these genes, Chlamydia trachomatis encodes only trpRBA. Tryptophan is degraded by the host enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) which can be induced by interferon-γ or constitutively expressed, most notably by foetal trophoblasts in the placenta. Adapted from Wood et al. (2004).