Figure 5. Normal levels of CNS myelin gene expression require Dync1h1 function.
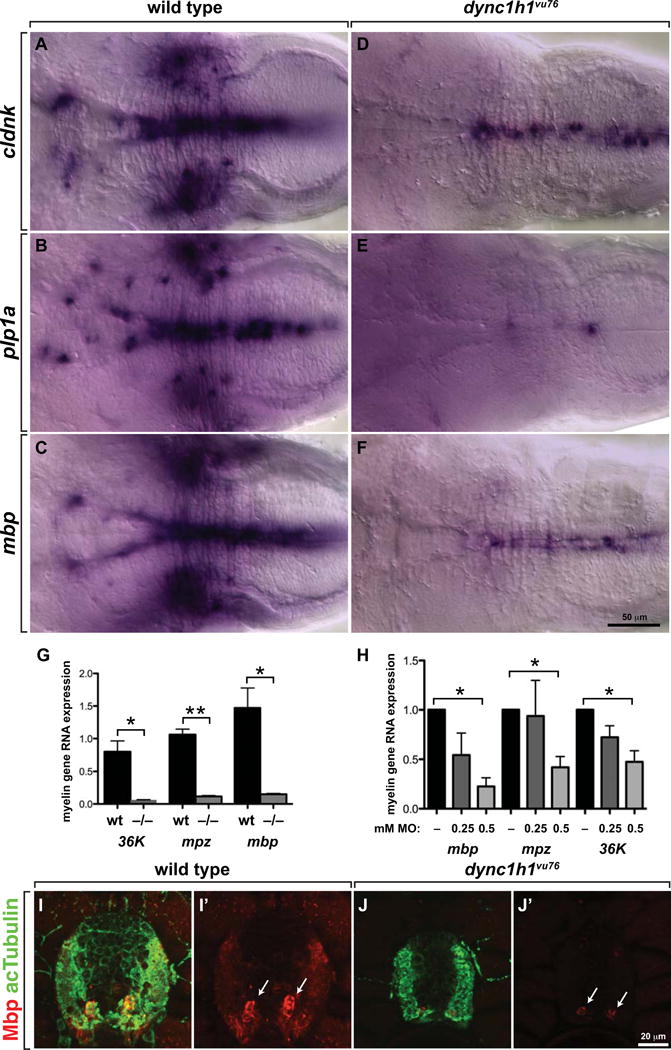
(A–F) Whereas 4 dpf wild-type larvae robustly express cldnk, plp1a and mbp RNA, only apparently low levels of transcripts are evident in similarly processed dync1h1vu76 mutant larvae. Images show dorsal views of whole larvae at the level of the midbrain and hindbrain, with anterior to the left. (G, H) Quantitative RT-PCR confirmed the deficit of myelin gene expression in dync1h1vu76 mutant larvae and dync1h1 MO-injected larvae. (I, J) Levels of Mbp (red), detected by immunohistochemistry, appear higher in wild-type spinal cord than in mutant spinal cord. Anti-acetylated Tubulin (green) reveals axons. Images show transverse sections, with dorsal up. Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired t test with Welsh correction. * P<0.05; ** P<0.001. Error bars represent + SEM.
