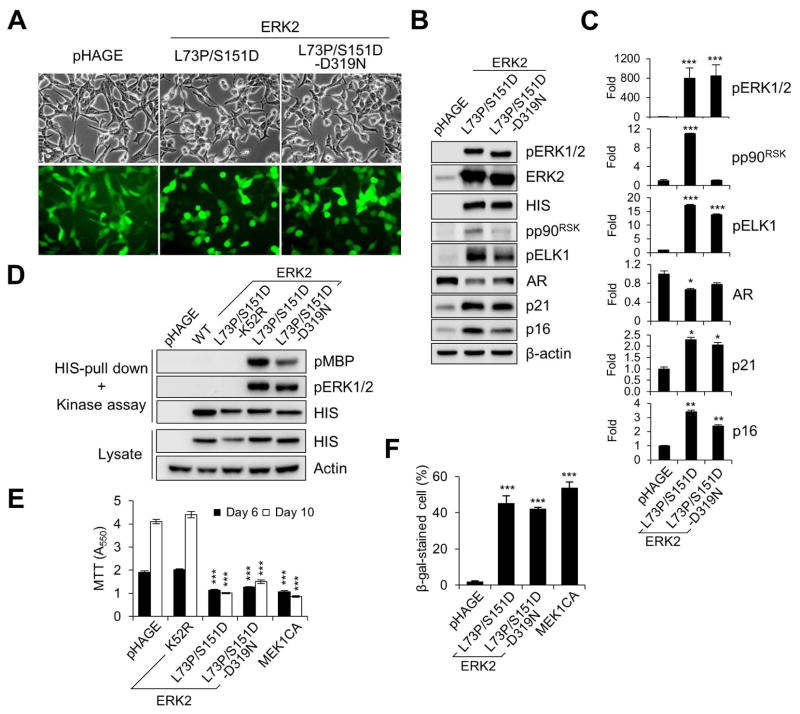
FIG. 3. Effects of sevenmaker mutation on ERK2-L73P/S151D signaling.
LNCaP cells were infected with lentivirus expressing wild type ERK2, ERK2-L73P/S151D, ERK2-L73P/S151D/D319N, ERK2-K52R/L73P/S151D, and MEK1CA. (A) Cells were observed for morphological changes at post-infection day 2. (B) Total cell lysates harvested at post-infection day 2 were analyzed by Western blotting for expression of the indicated proteins. (C) Densitometry of Western blot data in B. (D) In vitro kinase assay of HIS-tagged ERK2 isolated from cells. Kinase assay reaction and whole cell lysate were analyzed by Western blotting. Phosphorylation of the kinase substrate MBP (pMBP) indicates ERK catalytic activity. (E) Cell growth was monitored at post-infection days 6 and10 by MTT assay. (F) Senescence-associated acidic β-galactosidase activity was assayed at post-infection day 10. Data (means ± SE) are from a representative experiment performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (Student’s t-Test).