Table 1.
Optimization of pH dependence of GluN1/GluN2B antagonists as a function of N-alkyl chain length and steric bulk.
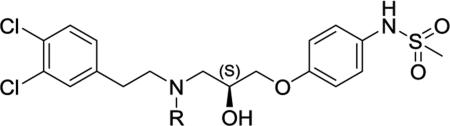
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra | # | Chain amine pKab | Fold increase in ionized speciesc | N-substituent Volume Angstroms3 | IC50 pH 6.9 H.M (N) d | IC50 pH 7.6 HM (N) d | IC50(7.6) /IC50(6.9) Ratio e |
| -H | (S) 93-4 | 8.6 | 1.1 | -- | 0.036 (10) | 0.045 (11) | 1.3 |
| -CH3 | (S) 93-2 | 8.0 | 1.3 | 19.8 | 0.050 (29) | 0.13 (22) | 2.6 |
| -CH2CH3 | (S) 93-5 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 33.4 | 0.021 (22) | 0.067 (14) | 3.2 |
| -CH2CH2CH3 | (S) 93-6 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 47.9 | 0.094 (17) | 0.48 (16) | 5.1 |
| -CH2CH2CH2CH3 | (S) 93-31 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 62.3 | 0.19 (32) | 1.8 (23) | 9.4 |
| -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 | (S) 93-87 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 77.5 | 0.16 (9) | 0.60 (6) | 3.8 |
| -CH(CH3)2 | (S) 93-115 | 8.2 | 1.2 | 47.9 | 0.19 (11) | 0.62 (12) | 3.3 |
| -CH2CH(CH3)2 | (S) 93-97 | 8.0 | 1.3 | 63.6 | 1.1 (21) | 3.2 (31) | 2.9 |
Compound synthesis described in Tahirovic et al., (2008); all compounds were the S enantiomer.
The pKa of the chain nitrogen was calculated using ACD/pKa DB 12.00, www.acdlabs.com.
Fold increase ionized species when reducing pH from 7.6 (pH1) to 6.9 (pH2) was calculated using equation (3): the Henderson-Hasselbach equation as (1 + 10(pH2 - pKa)) / (1 + 10(pH1 - pKa))
IC50 values for inhibition of GluN1/GluN2B expressed in Xenopus oocytes were determined as described in the Methods from composite inhibition curves. N is the number of oocytes recorded; measurements made for oocytes at both pH values in the same experiment. The slope varied between −0.70 to −1.09; maximum inhibition 79-100%.
The pH-dependent potency ratio for inhibition of GluN1/GluN2B receptors.
See also Figure S1 and Table S6.
