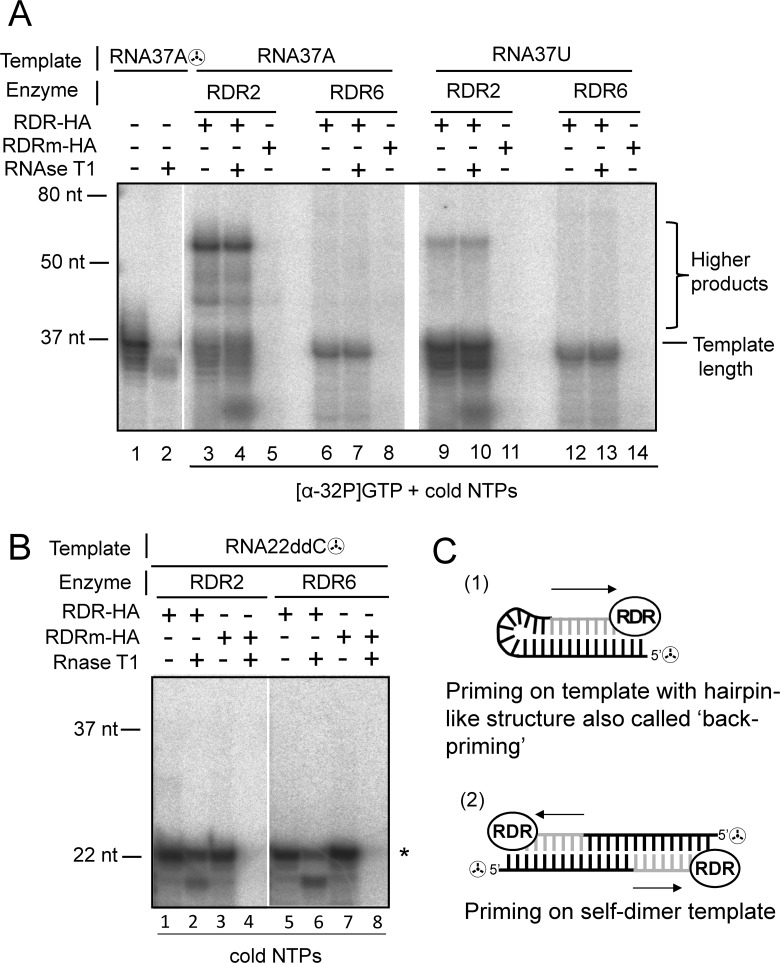
Fig 2. RDR2-HA and RDR6-HA initiate in vitro RNA synthesis using a de novo (primer-independent) mechanism.
(A) RNA polymerase assays of purified RDR2-HA and RDR6-HA on 37nt long ssRNA templates (RNA37A and RNA37U) in presence of cold NTPs and trace amount of [α32-GTP]. lane1: 5'[32P]-labeled RNA37A (RNA37A☢) is used as a size marker. lane2 RNA37A☢ treated with RNAse T1 as a control for RNAseT1 digestion in conditions that almost completely degrade the ssRNA template (B) Purified RDR2-HA and RDR6-HA were incubated with cold NTPs and a 22-nt 5’[32P]-labeled ssRNA template blocked at its 3′ end by dideoxycytidine (RNA22ddC☢). (*) A single star indicates the position of the 5’[32P]-labeled template. (C) Schematic representation of mechanisms that allow RNA polymerases to generate products higher than the RNA template size (“higher products”). Arrows indicate the direction of RNA polymerization. Template RNA in black, synthesized RNA by RDR in grey.