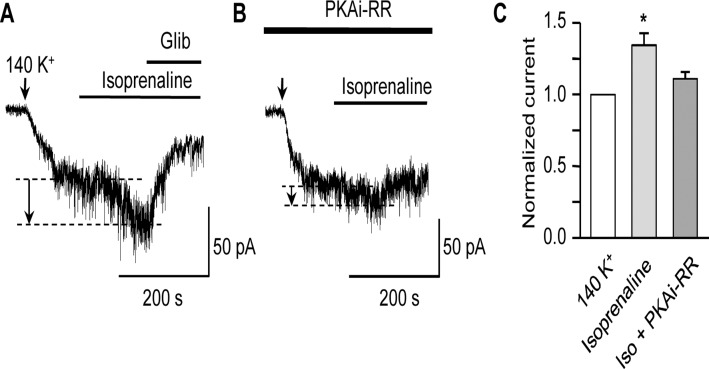
Fig 4. Isoprenaline activates KATP current in a PKA-dependent manner.
Representative KATP current traces obtained at -60 mV in symmetrical 140 mM K+ following the application of isoprenaline (100 nM) in the absence (A) or presence (B) of the active PKA inhibitor peptide (PKAi-RR, 5 μM) in the patch-pipette. Arrows in this and subsequent figures indicate the point at which extracellular [K+] was increased from 6 to 140 mM. The current increase in response to isoprenaline is indicated by the dashed lines and arrows. (C) Mean KATP current, (normalized to that in 140 mM K+) following the application of 100 nM isoprenaline in the absence (n = 6) or presence (n = 8) of PKAi-RR in the patch-pipette (*P<0.05; one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post hoc test).