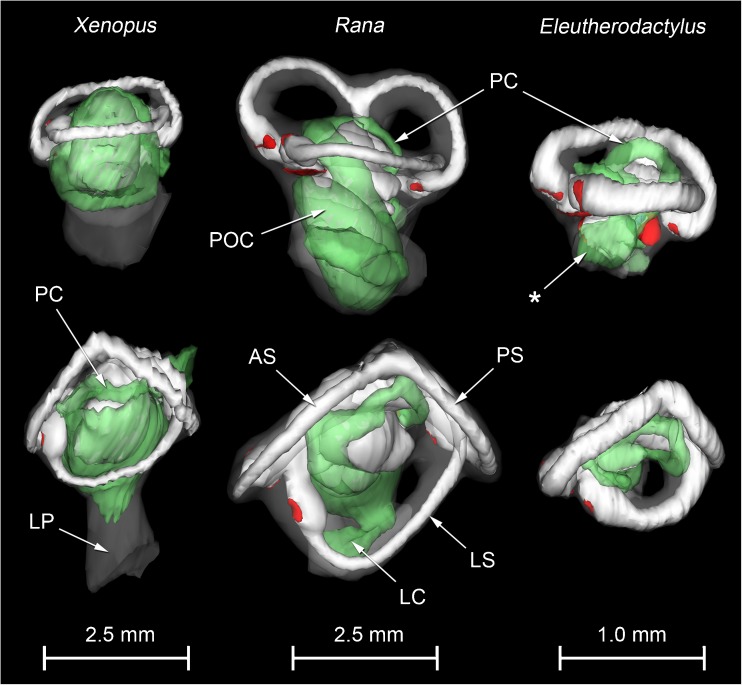
FIG. 2.
WinSurf reconstructions of the left inner ear structures of Xenopus laevis (left), male specimen, Rana pipiens (middle) and Eleutherodactylus limbatus (right). Lateral views are shown in the top row, dorsal views in the bottom row. Eleutherodactylus reconstructions are 2.5× enlarged relative to the others. In the Eleutherodactylus sections used for these reconstructions, the periotic cistern in the region marked with an asterisk, which lies lateral to the very small saccular cavity, had collapsed. Its approximate shape has been restored here by comparison with the contralateral ear and the extent of the space available for it within the otic capsule. Colour code: white = otic labyrinth (endolymph); green = periotic labyrinth (perilymph); red = sensory epithelium; semitranslucent grey = internal walls of the otic capsule. Key to this and subsequent figures: AR amphibian recess (endolymph), AS anterior semicircular canal, B brain, BR basilar recess (endolymph), CA contact membrane of amphibian recess, CB contact membrane of basilar recess, CC crus commune (confluence of anterior and posterior semicircular canals), CS contact membrane of saccule, IS inferior saccular chamber, LC lateral chamber, LP lateral passage, LR lagenar recess (endolymph), LS lateral semicircular canal, LT limbic tissue, O operculum, PC periotic canal, POC periotic cistern, POS periotic sac, PS posterior semicircular canal, PT periotic tissue, PU posterior utricular cavity, RPB recessus partis basilaris (perilymph), RW round window, S saccule, SPI stapes pars interna, SPM stapes pars media, SS superior saccular chamber, TV tegmentum vasculosum or the saccular diverticulum within which this epithelial lining is found, VIII branch of eighth cranial nerve.