Fig 2. Linear readout and its interpretation.
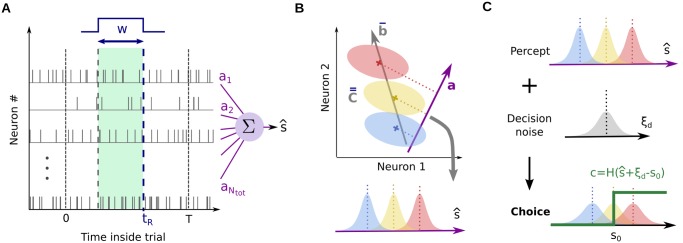
(A) We study a “standard” model of percept formation, with two parameters w and t R defining integration in time, and a readout vector a defining integration across neurons. (B) Geometric interpretation of the model. The temporal parameters w and t R define the tuning vector and noise covariance matrix in the population. Colored ellipses represent the distribution of neural activities from trial to trial, for the three possible stimulus values. The readout can be viewed as an orthogonal projection of neural activities in the direction given by a. (C) Behavioral part of the model. The percept can be corrupted by decision noise ξ d. Then it is thresholded to produce a binary choice c.
