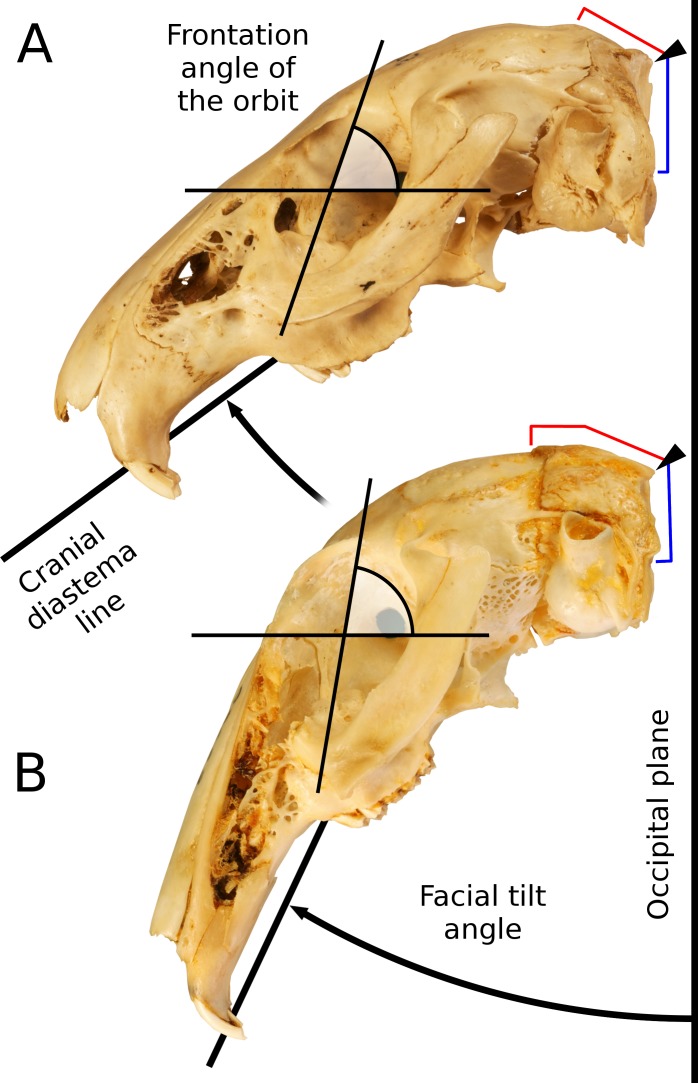
Figure 2. Facial tilt in leporids.
The crania of (A) Caprolagus hispidus (AMNH 54852, above) and (B) Pronolagus crassicaudatus (AMNH 89033, below) are shown in left lateral view. Facial tilt (FT) is defined herein as the angle between the upper diastema and the occipital plane, where increased values indicated a skull orientation closer the horizontal plane. The triangle indicates the position of the external occipital protuberance (EOP), and from that, both the dorsal (red) and occipital (blue) extent of the supraoccipital bones is outlined.