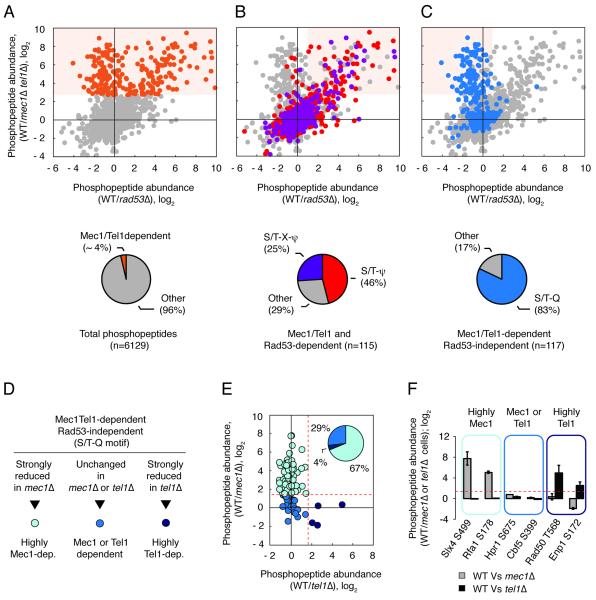
Figure 1. Proteome-wide identification of Mec1/Tel1-dependent phosphorylation events using quantitative MS.
(A) Identification of Mec1/Tel1-dependent phosphopeptides (cells treated with 0.2M HU or 0.04% MMS). Orange dots correspond to 238 Mec1/Tel1-dependent phosphopeptides. See text for details. (B) Mec1/Tel1 and Rad53-dependent phosphorylation events (light orange shade) are biased towards the S/T-ψ (red) and S/T-X-ψ (purple) motifs. (C) Mec1/Tel1-dependent and Rad53-independent phosphorylation events (light orange shade) are biased towards the S/T-Q motif (blue). (D-E) The phosphoproteome of WT cells was compared to the phosphoproteome of mec1Δ or tel1Δ cells (all cells treated with 0.04% MMS) and phosphopeptides carrying phosphorylation in the S/T-Q motif were categorized according to the observed change in abundance. Dotted red lines represent the established cutoff of 3-fold increase in WT relative to mec1Δ or tel1Δ cells. (F) Examples of phosphopeptides of each of the indicated groups. Data are represented as fold change in phosphopeptide abundance; log2 +/− SEM (n≥2). See also Table S1.