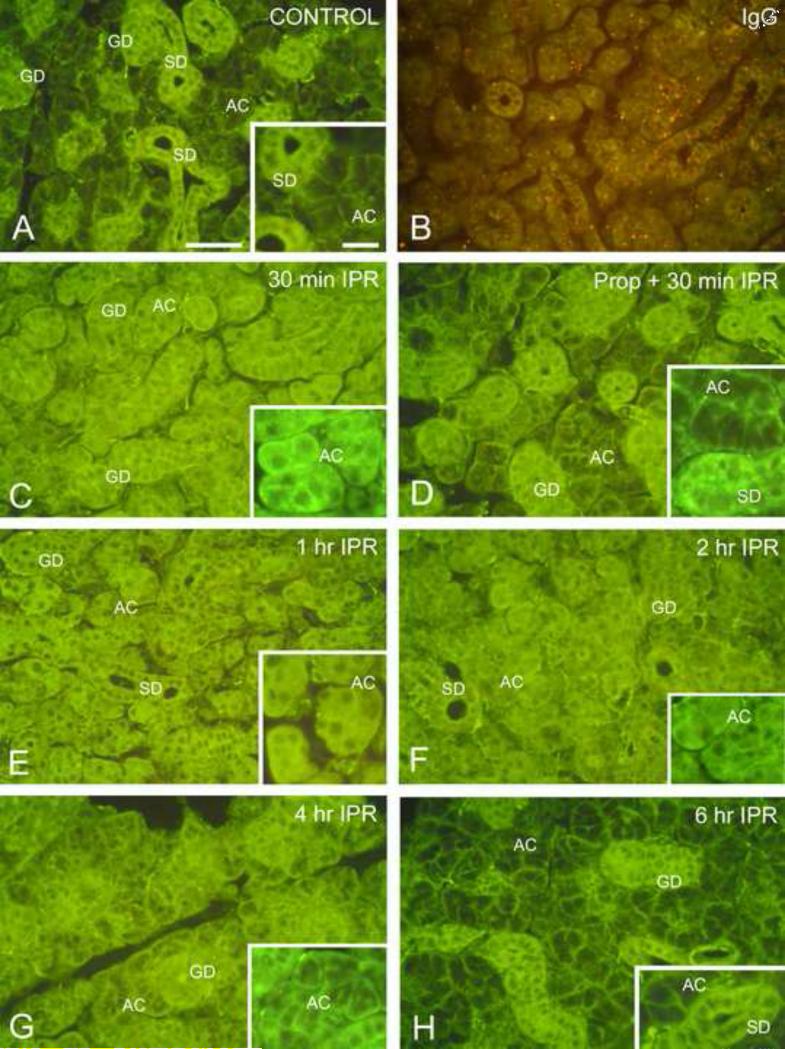
Figure 3.
Immunofluorescence localization of Gαs in mouse submandibular gland. Scale bars: main panels, 50 μm; insets, 20 μm. (For color reproduction on the Web and in print.)
A. Unstimulated control. In the secretory acinar cells (AC), Gαs is localized to the basolateral membranes of the cells; minimal cytoplasmic labeling is observed. Cells of the striated (SD) and granular (GD) ducts show strong cytoplasmic fluorescence.
B. Isoproterenol, 2 hr; incubated with non-immune IgG. Weak non-specific fluorescence is seen in the acini and ducts. Lysosomes exhibit orange autofluorescence.
C. Isoproterenol, 30 min. Most of the fluorescence in acinar cells (AC) is located in the cytoplasm; membrane-associated fluorescence is substantially reduced. Some apical fluorescence is seen in the striated and granular ducts (GD).
D. Propranolol/Isoproterenol, 30 min. Administration of the β-receptor antagonist, propranolol, 30 min prior to isoproterenol, reduces redistribution of Gαs. Most of the fluorescence in acinar cells (AC) is associated with the cell membranes, similar to the unstimulated control gland. Only low levels of fluorescence are present in the acinar cell cytoplasm. Fluorescence is present throughout the cytoplasm of striated (SD) and granular ducts (GD).
E. Isoproterenol, 1 hr. Fluorescence is present throughout the acinar cell (AC) cytoplasm; little or no membrane-associated fluorescence is seen. Apical labeling of striated (SD) and granular ducts (GD) is still apparent.
F. Isoproterenol, 2 hr. The acinar cells (AC) exhibit slightly decreased cytoplasmic fluorescence and increased membrane-associated fluorescence. Apical labeling of striated (SD) and granular ducts (GD) is still apparent.
G. Isoproterenol, 4 hr. Cytoplasmic fluorescence of the acinar cells (AC) is reduced, and membrane-associated fluorescence is increased. Granular duct (GD).
H. Isoproterenol, 6 hr. The distribution of fluorescence is similar to that of the unstimulated control gland. Most acinar cells (AC) show basolateral membrane-associated fluorescence, and minimal cytoplasmic fluorescence. Strong cytoplasmic fluorescence is seen in striated (SD) and granular ducts (GD), but apical fluorescence appears reduced.