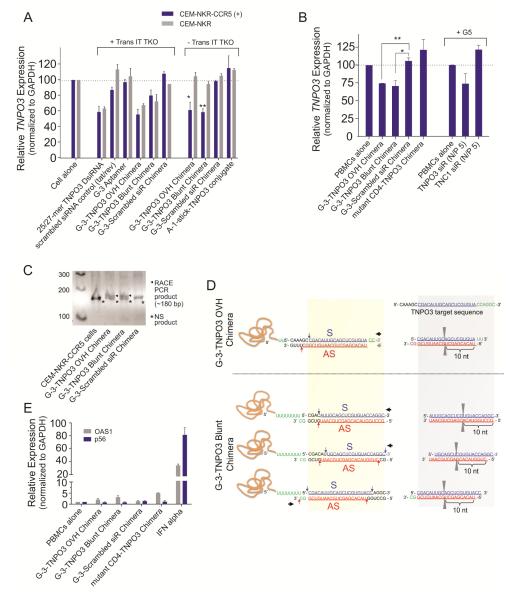
Figure 4. CCR5 aptamer delivered siRNAs specifically knockdown TNPO3 expression via RNAi pathway.
Relative TNPO3 mRNA expression was detected by real-time PCR in A) CEM-NKr-CCR5 and CEM-NKr negative cells, and B) human PBMC-CD4+ cells. As negative control, unrelated aptamer-siRNA chimera (gp120 aptamer A-1 or mutant CD4 aptamer) and G-3 aptamer-scrambled siRNA chimera were used. Asterisk indicates a significant difference compared with control (P < 0.01, student’s t-test). 5′-RACE PCR analysis of TNPO3 DsiRNA delivered by CCR5 aptamer – siRNA chimeras. C) Nested PCR products were resolved in an agarose gel and specific siRNA-mediated RACE PCR cleavage mRNA products are marked by a bold arrow. D) The positions of the siRNA directed cleavage sites in the TNPO3 target RNA are indicated with a pair of grey triangle. According to mRNA cleavage, these predicated siRNA species also are showed with blue and red arrow. The proposed directions of Dicer entry are indicated by a bold black arrow. E) IFN gene activation assays in human PBMCs. The interferon response genes encoding P56 (CDKL2) and OAS1, were measured by quantitative RT-PCR. These data represent the average of three replicate measurements.