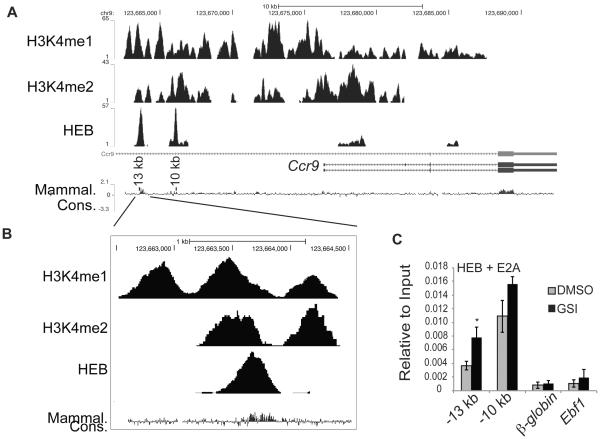
Figure 4. Identification of E protein binding sites near the Ccr9 gene.
(A) Occupancy by the HEB transcription factor as well as H3K4me1 and H3K4me2 at the Ccr9 locus, as determined by ChIP-seq and visualized by the UCSC browser. Schematic of the Ccr9 gene is shown below the ChIP-seq histograms. The UCSC track of sequence conservation in mammals is also shown and the −13 kb and −10 kb conserved regions are indicated. The chromosome locations are indicated above the tracks. (B) Enlarged view of the −13 kb conserved region showing the overlap between HEB binding, H3K4me1, and H3K4me2. (C) QPCR analysis of chromatin immunoprecipitated by antibodies directed against the E proteins HEB and E2A from the day 7 Lin−CD45+ progeny of FL-MPPs treated for 48hrs treated with DMSO (grey) or GSI (black). DNA was amplified using primers within the −13 kb and −10 kb conserved regions or using primers to β-globin or Ebf1, which served as negative controls. Data is expressed as enrichment normalized to input and is averaged from three independent experiments. * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01.