Figure 2.
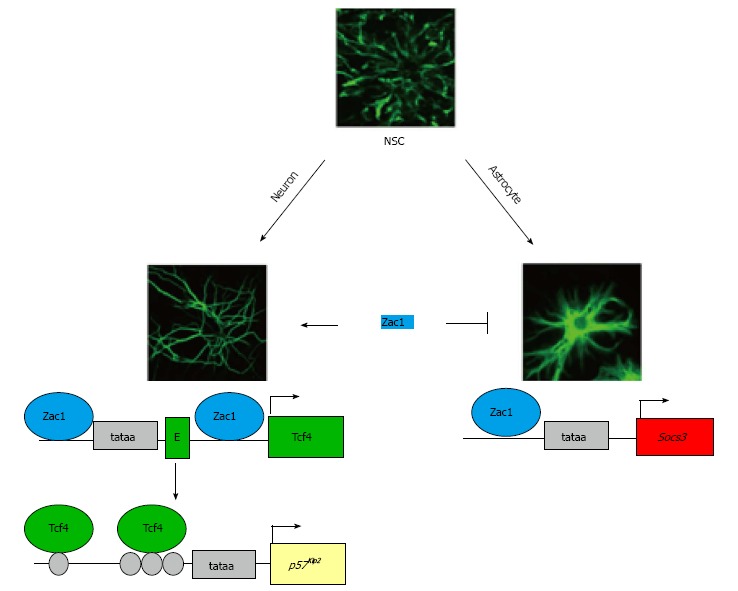
Imprinted Zac1 favors neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells. The Zac1 gene is maternally imprinted and encodes a versatile transcriptional regulator. Zac1 expression is strongly induced during neuronal and astroglial differentiation of embryonic and adult neural stem cells (NSCs). During neuronal differentiation (left scheme), Zac1 binds to GC-rich DNA binding sites at the Tcf4 promoter and first intron to confer synergistic transactivation. As a result, enhanced Tcf4 expression promotes binding to and transactivation of the cyclin kinase inhibitor p57Kip2, which induces G1 arrest. Moreover, Zac1 binds to GC-rich DNA elements at the Socs3 promoter during astroglial differentiation (right scheme). Socs3 encodes a potent inhibitor of prodifferentiative Jak/Stat3 signaling and prevents precocious astroglial differentiation. The tataa-elements are boxed in light grey and the transcriptional start sites are symbolized by arrows. The first exon in the Tcf4 locus is depicted as a green box (labeled E) and coding exons of Tcf4 and Socs3 as green and red boxes, respectively. Tcf4 binds to various E-box motifs (light grey circles) localizing to the p57Kip2 regulatory region.
