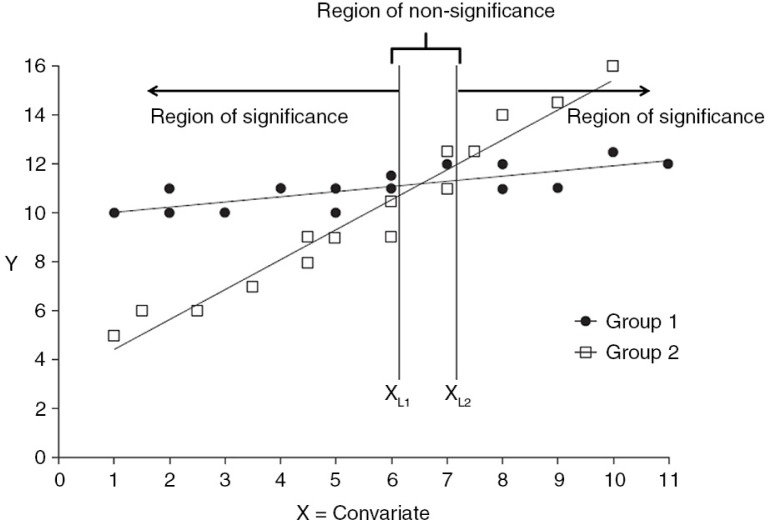
Fig. 1.
The Johnson-Neyman technique. When heterogeneous regression slopes are present this implies that the magnitude of the intervention effect (Y) is not the same at different levels of X (covariate; the baseline intake in these analyses). The Johnson-Neyman approach provides values on X associated with non-significant/significant effects, giving regions of non-significance and significance. XL1 is the lowest value and XL2 is the highest value of the non-significance region.