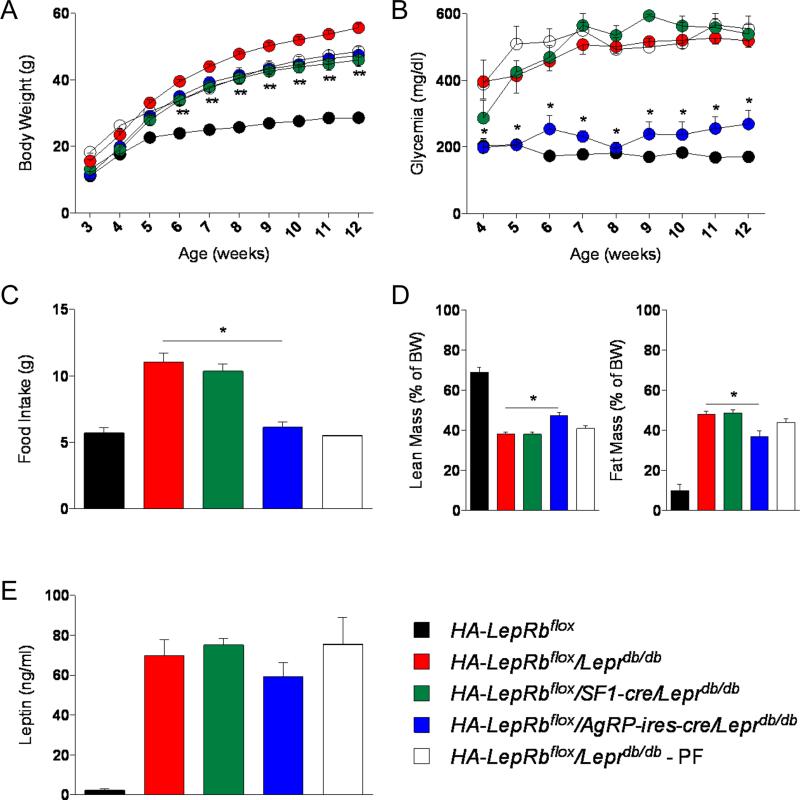
Figure 1. LepRbs in AgRP neurons, but not in SF1 neurons, are sufficient in mediating leptin's anti-diabetic actions.
(A-E) Body weight (A), glycemia (B), food intake (9 weeks of age) (C), body composition (10-12 weeks of age) (D) and serum leptin levels (E) in HA-LepRbflox, HA-LepRbflox/Leprdb/db, HA-LepRbflox/SF1-cre/Leprdb/db, HA-LepRbflox/AgRP-ires-cre/Leprdb/db and HA-LepRbflox/Leprdb/db - PF male mice. PF, pair-fed (5-12 weeks) to lean control mice. Errors bars are shown as SEM (n = 3-8/group). Statistical analyses were done using one-way or two-way ANOVA (Bonferroni post-hoc analyses). *p < 0.05 HA-LepRbflox/AgRP-ires-cre/Leprdb/db versus HA-LepRbflox/Leprdb/db mice; **p < 0.05 HA-LepRbflox/SF1-cre/Leprdb/db or HA-LepRbflox/AgRP-ires-cre/Leprdb/db versus HA-LepRbflox/Leprdb/db mice. See also Figure S1, S2 and S3.