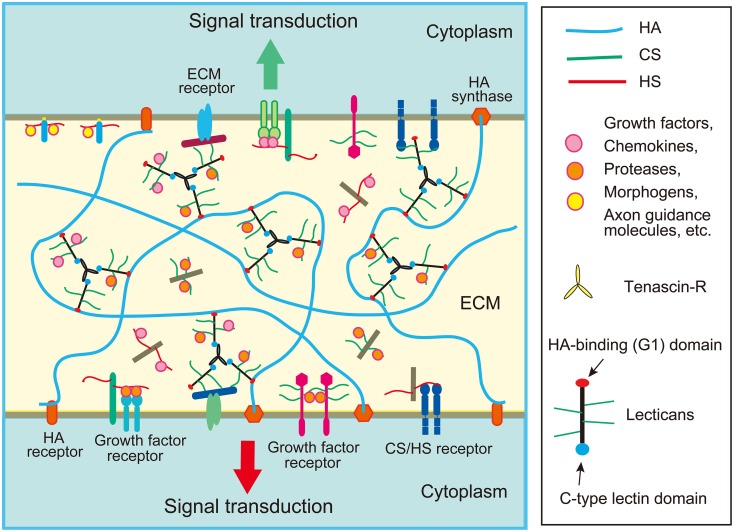
Figure 1.
Schematic structure of extracellular matrix (ECM) in the brain. The ECM of the brain is mainly composed of chondroitin sulfate (CS) and heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycans, hyaluronic acid (HA), and glycoproteins such as tenascins. Lectican family CS proteoglycans form large aggregates with HA and tenascins, which store various proteins such as chemokines, growth factors and axon guidance molecules. The ECM proteoglycans may bind with a CS/HS receptor on the cell surface such as RPTPσ. Cell surface proteoglycans may function as receptors or co-receptors for growth factors.