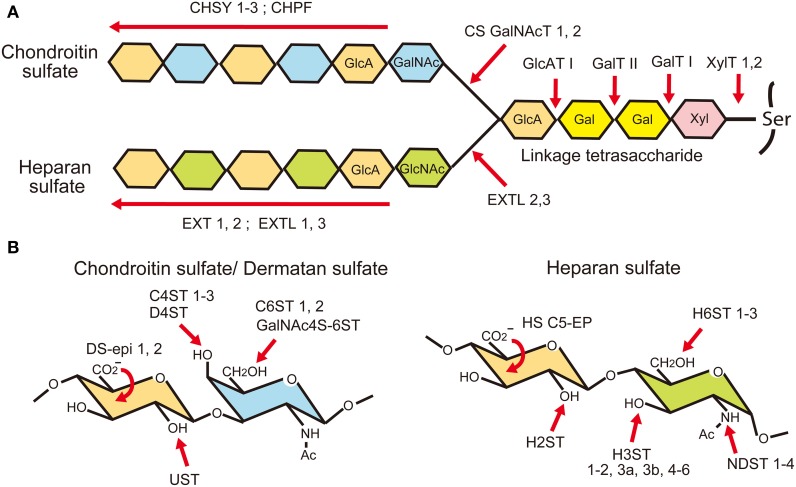
Figure 3.
Biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans. (A) Chondroitin sulfate (CS) and heparan sulfate (HS) chains are covalently attached to the proteoglycan core proteins through a common linkage tetrasaccharide. It is considered that the biosynthesis of a chondroitin chain starts with the addition of an N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) residue to the linkage tetrasaccharide by CS N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases (CSGalNAcT1, 2). After that, glucuronic acid (GlcA) and GalNAc residues are co-polymerized by chondroitin sulfate synthases (CHSY-1, -2, -3) and chondroitin polymerization factor (CHPF). When an N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residue is added to the linkage tetrasaccharide instead of GalNAc by EXTL 2 or 3, a heparan chain is polymerized by EXT family members. (B) After polymerization, they are modified by sulfation and epimerization reactions by many glycosaminoglycan modifying enzymes.