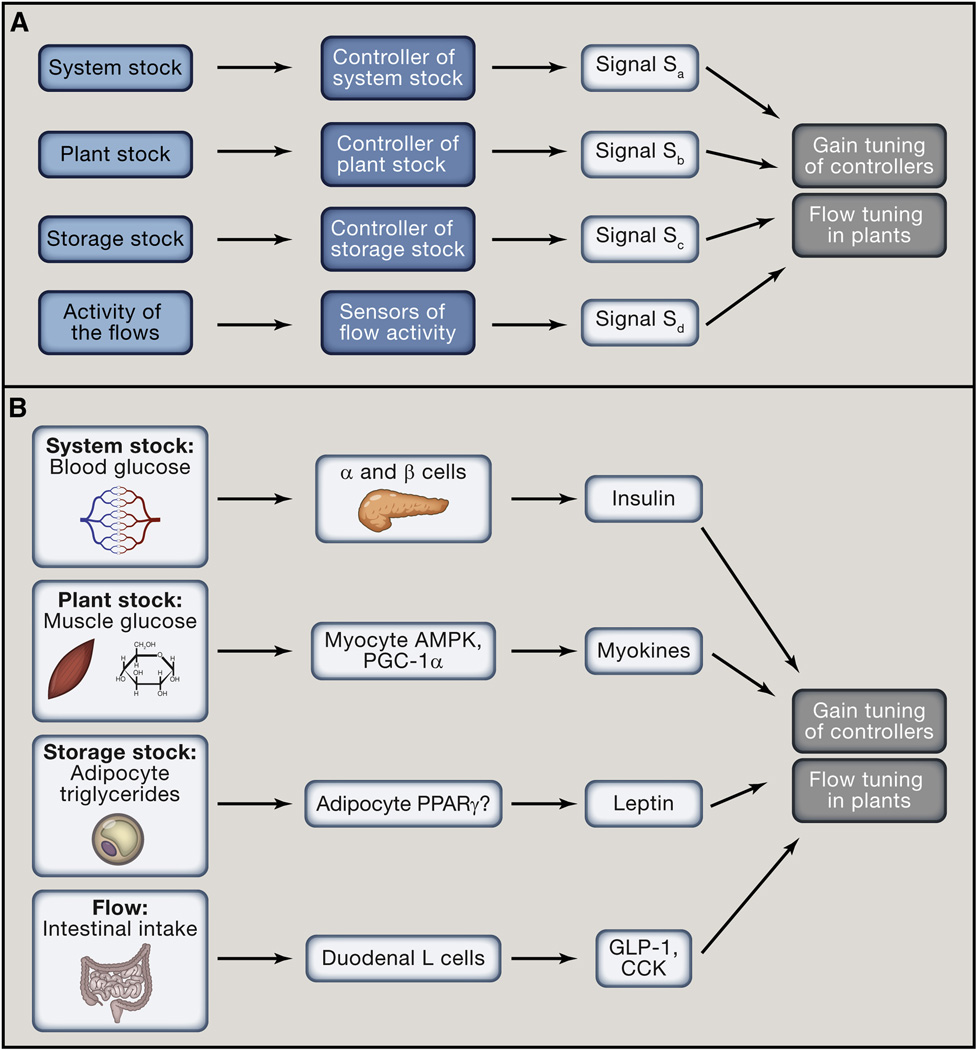
Figure 4. Four classes of signals control systemic homeostasis.
(A) Four classes of homeostatic signals report on values of four different types of variables: System stock (regulated variable), Plant stock, Storage stock and Flows. Each stock and the flows are monitored by dedicated Controllers and sensors. All four categories of homeostatic signals modulate gain tuning of Controllers and flow tuning in Plants. Signals that report on stocks operate in feed-back loops. Signals that report on flows operate in feed-forward loops.
(B) Signals reporting on the System stock (Sa) are classical endocrine hormones and efferents of the autonomic nervous system (e.g., insulin and glucagon). Signals reporting on Plant stocks (Sb) primarily operate in a cell or tissue autonomous manner (e.g., AMPK controlling GLUT4 expression), but may include signals acting systemically (e.g., AMPK controlling IL-6 expression in exercising muscle). Signals reporting on Storage stocks (Sc) indicate available resources (e.g., leptin reporting on fat stores). Finally, signals reporting on Flows (Sd) indicate anticipated changes in the System stock (e.g., GLP-1 reporting on incoming glucose). The examples are chosen to illustrate the point.