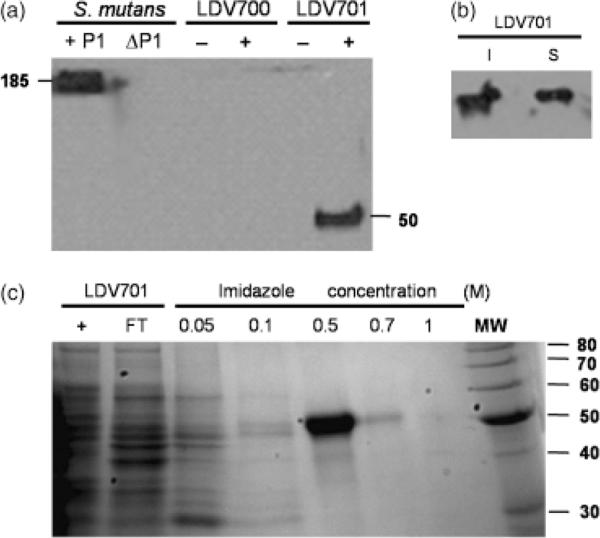
Fig. 2.
Detection and purification of the recombinant P139–512 protein expressed by Bacillus subtilis cells. (a) Immunodetection of P1 or P139–512 expressed by Streptococcus mutans PC3370C (1P1) or B. subtilis LDV701 (LDV701) strains, respectively. Negative controls include S. mutans PC3370 (ΔP1) and the B. subtilis LDV700 strain (LDV700). − and + denote cells induced or not with IPTG, respectively. Estimated molecular weights (kDa) of the reactive protein bands are indicated. (b) Immunodetection of recombinant P139–512 in the soluble (S) or insoluble (I) fractions of the B. subtilis LDV701 following induction with IPTG. (c) Purification of recombinant P139–512 expressed in B. subtilis. Imidazole concentrations used to elute the protein from the nickel-containing resin are indicated. Proteins were separated in 12.5% polyacrylamide gels and stained with Comassie Brilliant Blue. MW, molecular weight markers indicated in kilodaltons (kDa) at the right side of the figure.