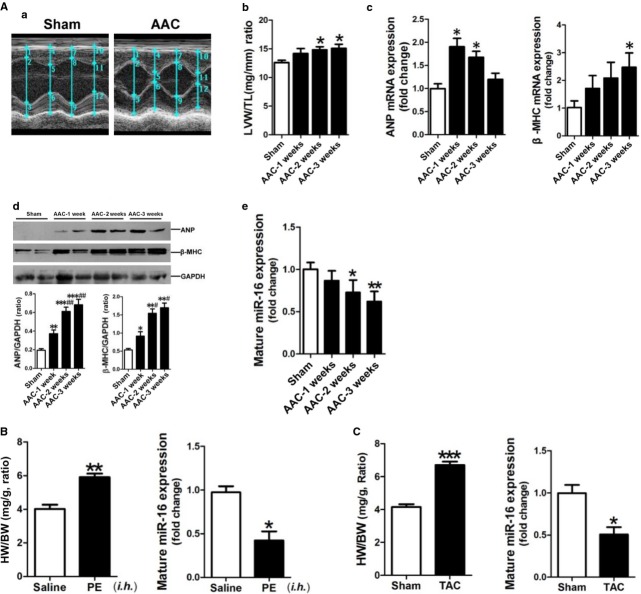
Fig 1.
miR-16 is down-regulated in hypertrophic myocardium. (A) Establishment of a rat model of AAC-induced hypertrophy. (a) Representative echocardiographs showing that the LVAWd, LVAWs, LVPWd and LVPWs were increased in the hearts of rats in the AAC group. The detailed data were presented in Table S1. (b) The ratio of LV weight to tibial length. (c) ANP and β-MHC mRNA expressions were assessed by qRT-PCR assay (n + 6–8). (d) ANP and β-MHC protein expressions were assessed by Western blotting assay (n + 6–8). (e) Mature miR-16 expression was determined by qRT-PCR assay (n + 6–8). (B) The ratio of heart weight to bodyweight, and mature miR-16 expression in the myocardium of a mouse model of PE-induced cardiac hypertrophy by qRT-PCR (n + 6–8). The C57BL/6 mice were given subcutaneous injections of PE at 20 mg/kg/day for 3 days. The mice were then maintained for another 7 days, followed by cervical dislocation and removal of the hearts for subsequent analyses. (C) The ratio of heart weight to bodyweight, and mature miR-16 expression in the myocardium of a mouse model of TAC-induced cardiac hypertrophy as detected by qRT-PCR (n + 6–8). Data are shown as mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus the Sham control or the Saline control, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the AAC-1 w group, respectively.