Fig 1.
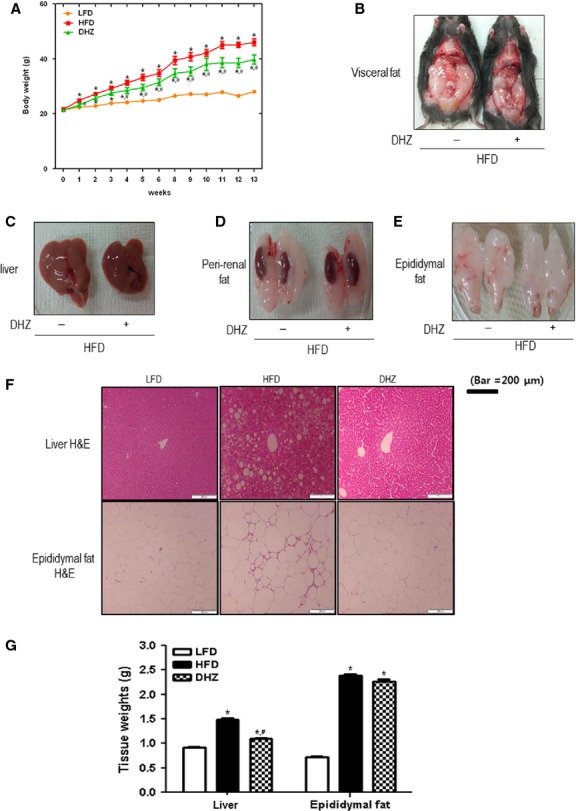
DHZ suppressed high-fat diet (HFD)-induced bodyweight gain. (A) Effects of DHZ on bodyweight in an HFD-induced obesity model. Data are provided in terms of means ± SD (n + 5). * Denotes significant differences compared with normal diet-fed mice (P < 0.05); *, # denotes significant differences compared with HFD-fed mice (P < 0.05). (B) Effects of DHZ on visceral fat in an HFD-induced obesity model. (C) Effects of DHZ on fatty liver in an HFD-induced obesity model. (D) Effects of DHZ on the kidney and peri-renal fat in an HFD-induced obesity model. (E) Effects of DHZ on the epididymal fat in an HFD-induced obesity model. (F) Effects of DHZ on the size of adipocyte of an HFD-induced obesity model. (G) Effects of DHZ on the weight of liver and epididymal fat tissues of an HFD-induced obesity model. The three groups were as follows: LFD, low-fat diet; HFD, high-fat diet and HFD supplemented with 100 mg/kg/day DHZ.
