Figure 4.
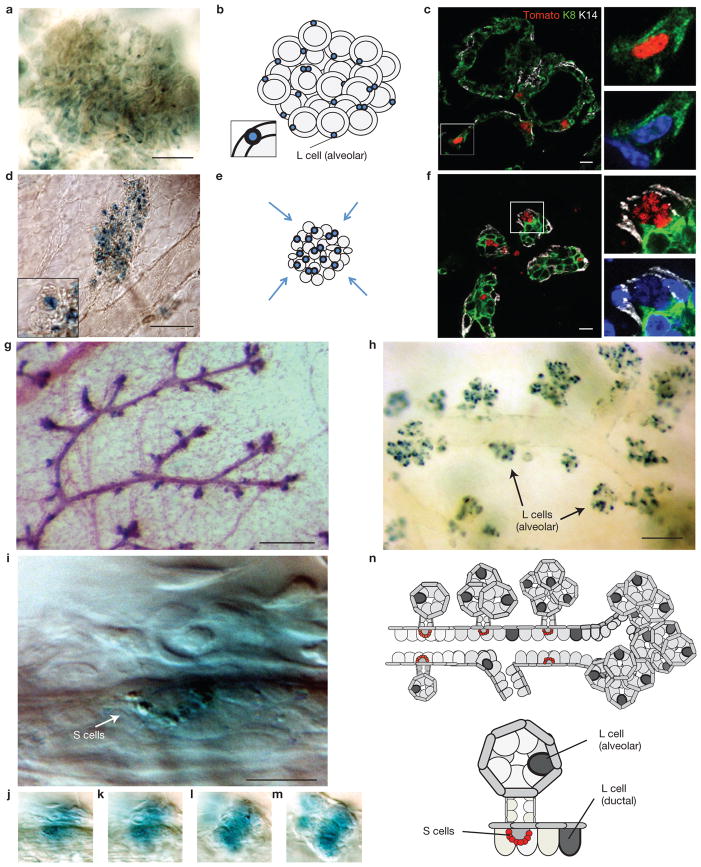
The fate of pubertal Notch2+ lineages during lactation and involution. (a–f) A typical alveolar cluster in lactating (a–c) and involuting (d–f) glands. N2-CreERT2SAT/R26RLacZ (a,d) and N2-CreERT2SAT/R26RTom (c,f) females induced with 4-OHT at 7 weeks of age and euthanized during lactation (a–c) or 4 days after forced weaning (d–f). x-gal-labelled whole-mount preparations (a,d), schematic presentations of alveolar cluster (b,e) and immunofluorescence micrographs of sections labelled with anti-K8 and anti-K14 antibodies showing several individual alveoli. Nuclei co-labelled with DAPI (c,f). The inset in b is a close-up of the alveolar L cell. Small panels in c and f are close-ups of the respective areas marked with the rectangle. The inset in d is a close-up of the collapsed alveolus. (g–m) x-gal-labelled mammary gland whole-mount preparations from N2-CreERT2SAT/R26RLacZ females induced at 7 weeks of age and euthanized in early pregnancy (8 dpc; g,i–m) or 4 days after forced weaning (h). (g,h) Budding tertiary branches (g) and alveolar clusters originating from primary and secondary ducts (h) are positioned at regular intervals alongside ductal longitudinal axis. (i) High-magnification image of an S cell string (arrow) in a large duct. (j–m) Different focal depths of the image shown in i. Beneath the S cells is an alveolar cluster consisting of several sprouting alveolar buds all of which are transiently filled with LacZ+ cells. (n) Schematic representation of the location of L (ductal and alveolar) and S cells in the lactating mammary gland. Gland in g is co-stained with carmine alum. Scale bars, 100 μm (a,d,h); 10 μm (c,f); 200 μm (g); 20 μm (i).