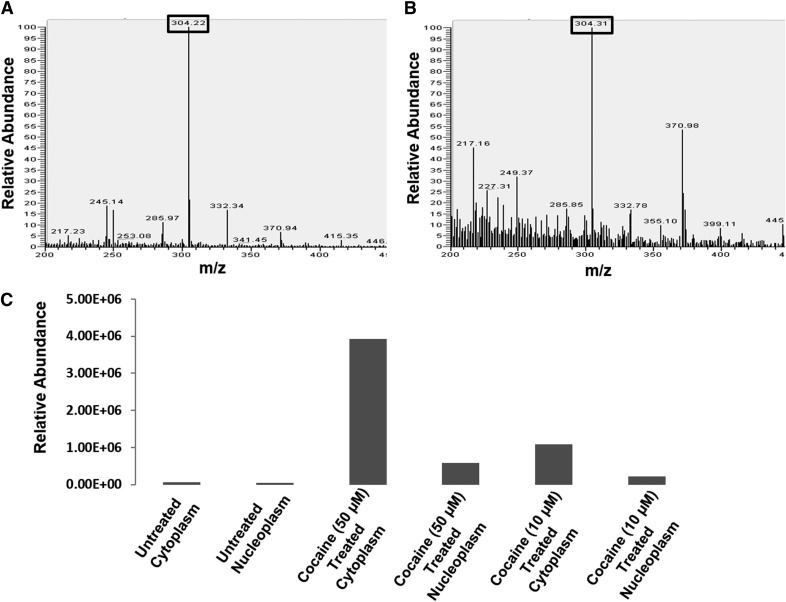
Figure 5. ESI LC-MS detection of cocaine in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of CD4+ T cells.
SupT1 cells were cultured in the absence or presence of cocaine overnight. Then, the cells were pelleted and washed, and cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were isolated after removing high molecular weight cellular debris. These fractions were extracted in a chloroform-methanol mixture (2:1, v/v) and analyzed by ESI LC-MS. The parent MS peaks of cocaine (304.2 m/z) were detected in (A) the cytoplasmic and (B) the nuclear fractions of cocaine-treated cells. (C) Relative abundance of cocaine in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of SupT1 cells treated with 10 µM and 50 µM cocaine. Relative abundance was calculated by comparing the detected parent peak of cocaine peak in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of treated cells to untreated cells. These data demonstrated that relative abundance of cocaine in the cytoplasm and nuclear fractions increased in a dose-dependent manner.