Figure 7.
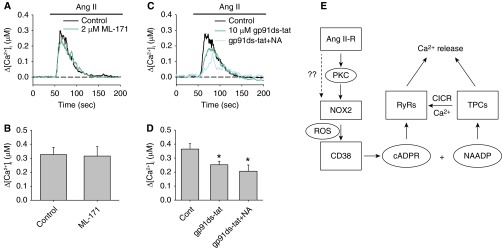
Effects of NOX1 and NOX2 specific antagonist on AICR in PASMCs. (A and B) The effect of the NOX1-specific inhibitor ML171 (30 μM) on AICR in PASMCs. (C and D) The effects of the NOX2-specific peptide inhibitor gp91 ds-tat (10 μM) on AICR in PASMCs in the absence or presence of NA (n = 8–13 experiments in each group). (E) A schematic diagram showing the proposed signaling pathways for AICR. *Significant inhibition of AICR compared with control. There was no significant different between gp91 ds-tat and gp91 ds-tat+NA–treated cells. CICR, Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release; NAADP, nicotinic acid adenosine dinucleotide phosphate; RyR, ryanodine receptor; TPC, two-pore channel.
