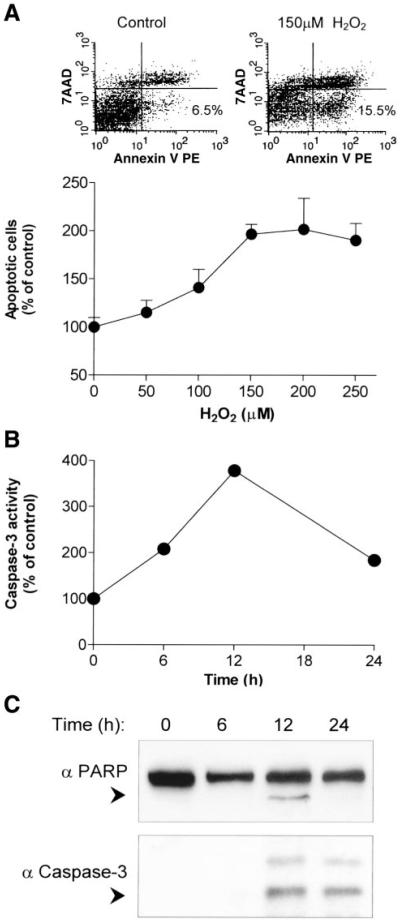
Fig. 3.
Pulse exposure of A549 cells to H2O2 induces caspase-3 activation and apoptosis. A: A549 cells were exposed for 1 h to increasing concentrations (50–250 µM) of H2O2 followed by incubation for 24 h in media supplemented with 10% FBS. Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry, as described in materials and methods. Top: illustration of annexin V/7-AAD staining of A549 cells, untreated (control) or treated with 150 µM H2O2. Values are presented as percent (%) of total cells counted (5,000). Scale bars represent the relative fluorescence intensity of the indicated dyes. Bottom: the values are presented as percent (%) of control, untreated cells and represent means + SE. B: A549 cells were exposed to 150 µM H2O2 for 1 h followed by incubation for the indicated time points with media containing 10% FBS. Caspase-3 activity was quantified by fluorometric immunosorbent enzyme assay (FIENA) as described in materials and methods. The values are presented as percent (%) of control untreated cells. C: A549 cells were induced as in B for the indicated time points. Then, cells were lysed and proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using antipoly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (anti-PARP, top) or anticleaved caspase-3 (bottom) antibodies. Arrowheads indicate the migration distance of PARP and caspase-3 cleaved forms.