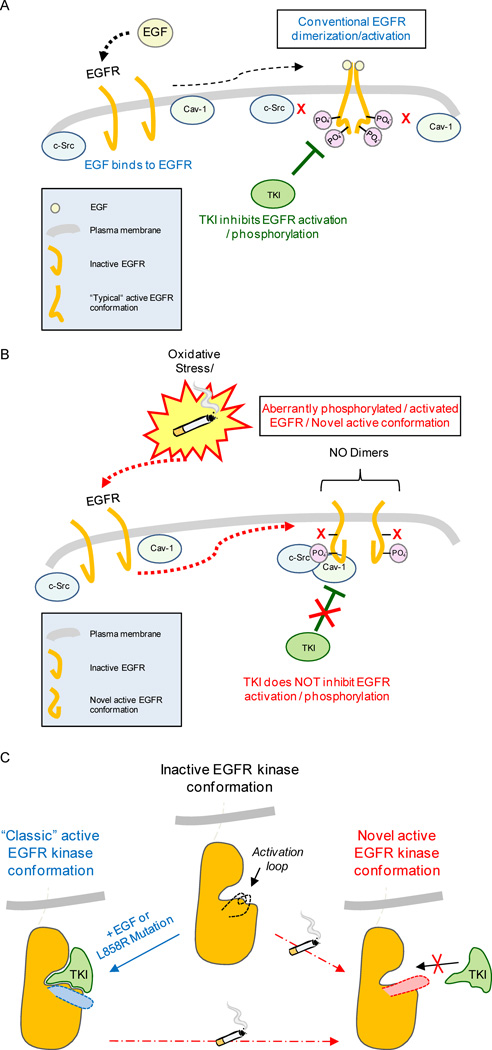
Figure 6. Proposed model of EGFR aberrant activation in lung epithelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke (CS).
A. Scheme of the conventional mechanism of activation/dimerization and phosphorylation of EGFR upon stimulation by the ligand EGF; activation/phosphorylation at specific tyrosine residues can be inhibited by TKI drugs. B. CS aberrantly activates EGFR, inducing aberrant phosphorylation* accompanied by a novel active conformation of the receptor that is bound by active c-Src and caveolin-1 (Cav-1)*. Such aberrantly activated EGFR does not dimerize “conventionally” and becomes resistant to TKI drugs. *Please note: aberrant phosphorylation of EGFR and Cav-1 binding to EGFR under CS-induced ox-stress were demonstrated by our group before (5, 18). C. Modeling EGFR structure/function alterations and change in conformation that may lead to TKI resistance following CS exposure.