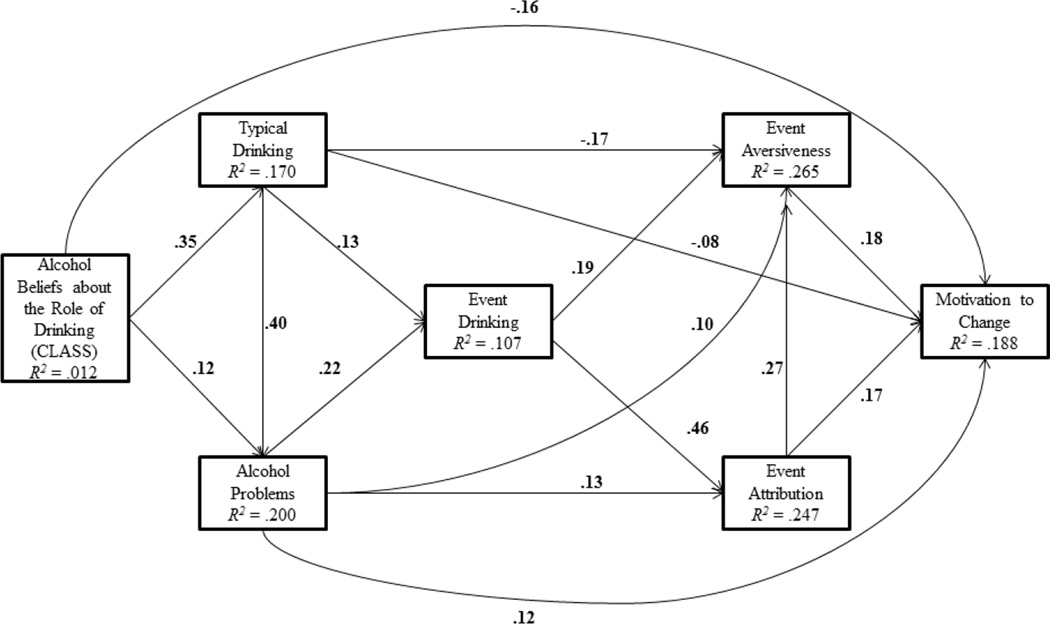
Figure 1.
Path model of associations among alcohol beliefs about the role of drinking in college as measured by the College Life Alcohol Salience Scale (CLASS), alcohol use involvement variables (typical drinking and alcohol problems), event-specific variables (event drinking, event attribution, event aversiveness), and motivation to change. Only significant effects (p < .05) are shown. Gender was controlled for by entering it as an exogenous predictor of all study variables; these effects are not shown for clarity.