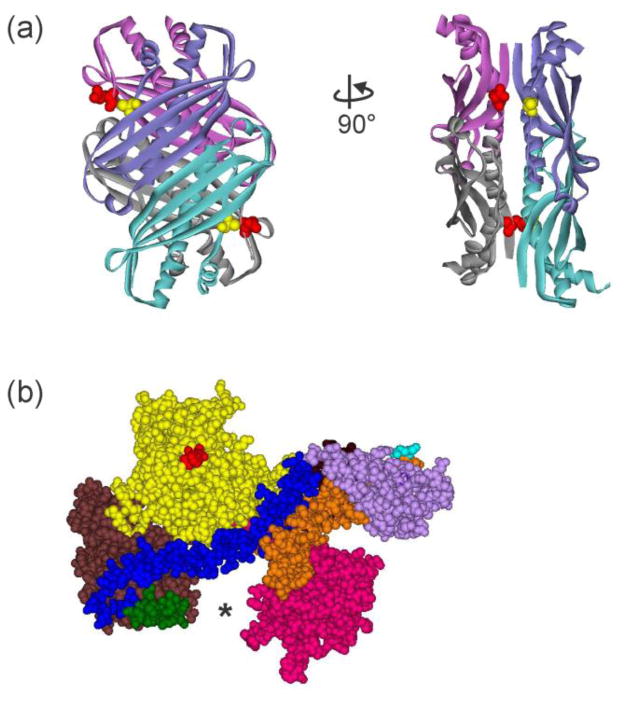
Figure 2. Structures of SecB and SecA.
(a) Structure of tetrameric SecB in ribbon representation from E. coli (Protein Data Bank [PDB] code 1QYN). The image on the right corresponds to a 90° rotation counterclockwise around the y-axis. SecB is structurally a dimer of dimers. One dimer, blue and blue-green protomers forming an eight-stranded β sheet, associates with the other dimer of purple and gray protomers via α helices on the interface. The residues altered to Cys to use in the creation of stable heterotetramers through introduction of disulfide bonds are shown as CPK models, Q12 (red) on the purple:gray dimer and A129 (yellow) on the blue:blue-green dimer. (b) Structure of SecA protomer in CPK models from E. coli protein. PDB code 2FSF with the PBD modeled in by A. Economou based on B. subtilis SecA PDB code ITF5. The separate domains are colored: Nucleotide Binding Domain (NBD) I (yellow), NBD2 (brown), 600 region (green), Helix Scaffold Domain (blue), Precursor Binding Domain (PBD, pink), two helix finger (orange), Helical Wing Domain (HWD, lavender). The location of the N terminus, the first residue resolved is Val 9, is indicated by the red CPK models. The final 65 residues from the C terminus were not resolved but would emerge from residue Glu 836 (cyan).