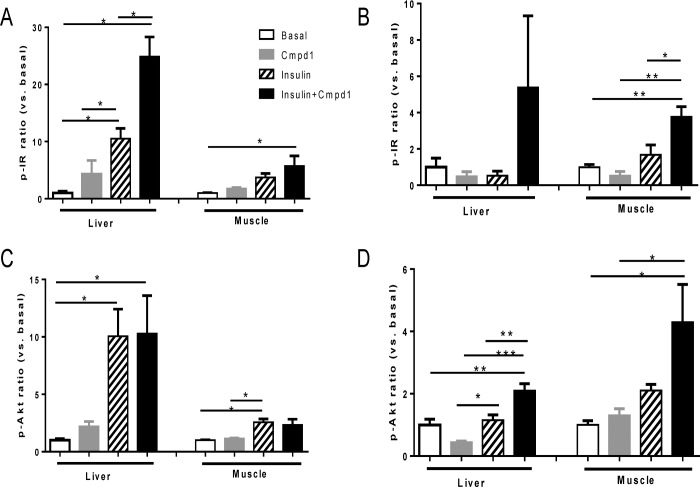
Fig 3. Cmpd1 has differential effects on insulin signaling in diabetic and normoglycemic tissues.
Mice were fasted for 4 hours and received Cmpd1 i.p. and 1 U/kg insulin administration at time 0. 30 min post injection, liver and gastrocnemius muscle were collected to examine insulin signaling. Tissue lysate phospho-protein analysis was conducted using phosphor-IR (Y1150/1151) from Cell Signaling Technology and phospho-Akt (Ser473) Assay kit from Meso Scale Technology. Fold changes of compound treated vs. basal untreated samples were calculated for pIR normoglycemic mice (A), pIR diabetic mice (B), pAkt normoglycemic mice (C) and pAkt diabetic mice (D). Basal liver pIR and pAkt levels in STZ-diabetic mice were ~3 fold higher than that in normoglycemic mice but overall magnitude of stimulation by insulin or Cmpd1 insulin combination are comparable in the two models. Basal muscle pIR and pAkt levels are similar in the two models. Results shown are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. comparators as indicated; n = 4 per condition.