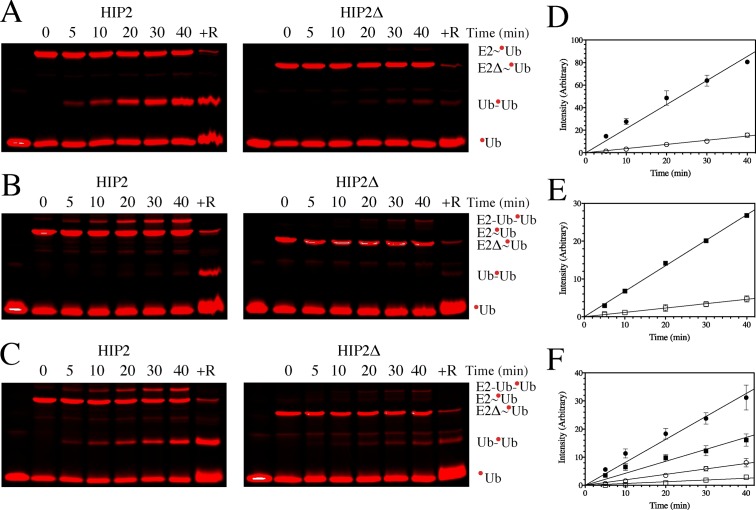
Fig 5. Time course reactions for HIP2~Ub thioester reactivity.
Fluorescent images of SDS gels for the reaction of Alexa-labeled HIP2~UbK48R (left) or HIP2Δ~UbK48R (center) with non-fluorescently labeled (A) ubiquitin, (B) HIP2–UbCys, or (C) equimolar amounts of ubiquitin and HIP2–UbCys. The initial lane in each reaction shows the Alexa-labeled UbK48R alone. Fluorescently-labeled HIP2~UbK48R and HIP2Δ~UbK48R were formed through a 20 min reaction at 37°C with HIP2 or HIP2Δ and Alexa-labeled UbK48R as described in the Experimental Procedures. Thioester formation was halted with EDTA (time = 0 min) and then reacted with either ubiquitin, HIP2–UbCys or both and samples measured at 5, 10, 20, 30 and 40 min. Reducing agent (10 mM DTT and 10 mM TCEP) was added to the 40 min sample (+R). Red circles denote the Alexa-labeled UbK48R molecule in each reaction. Also shown are the measured fluorescence intensities for (D) Ub2 formation from HIP2~UbK48R (●) or HIP2Δ~UbK48R (◯◻, (E) HIP2-Ub2 formation for HIP2~UbK48R (■) or HIP2Δ~UbK48R (◻) and (F) competing reactions forming Ub2 (●,◯) and HIP2-Ub2 (■,◻) from HIP2~UbK48R (●,■) or HIP2Δ~UbK48R (◯,◻) plotted as a function of time. Linear regression was used to fit each data set to approximate the initial product formation and the relative rates were determined by taking the ratio of the slopes. Each reaction was done in duplicate.