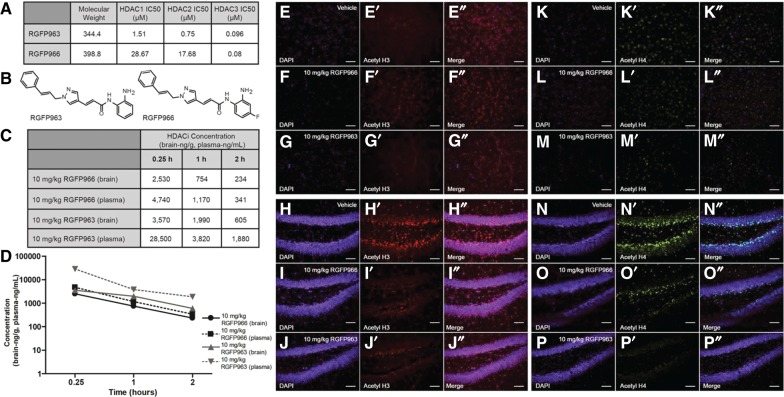
Figure 1.
RGFP963 and RGFP966 compound properties in vitro and in vivo. (A) RGFP966 exhibits specific inhibition of HDAC3, while RGFP963 broadly inhibits HDAC1, HDAC2, and HDAC3 in vitro. (B) Chemical structures of RGFP963 and RGFP966. (C,D) Of note, 10 mg/kg RGFP966 and RGFP963 are detected 0.25, 1, and 2 h post-IP injection (n = 3/group). Of note, 10 mg/kg RGFP966 is capable of inhibiting HDAC3, while minimally inhibiting HDAC1 and HDAC2, at the various time points assessed. Of note, 10 mg/kg RGFP963 is capable of inhibiting HDAC1, HDAC2, and HDAC3 at the various time points assessed. (E–P″) Vehicle, 10 mg/kg RGFP966, and 10 mg/kg RGFP963 were administered IP (n = 2/group). Subjects were perfused 1 h after drug administration and then tissue was processed for immunocytochemistry to determine an effect of drug on global H3 and H4 acetylation levels in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) and dentate gyrus (DG) region of the hippocampus. (E–E″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (E) and global acetyl H3 (E′) in the BLA with vehicle administration (E″ merged). (F–F″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (F) and global acetyl H3 (F′) in the BLA with 10 mg/kg RGFP966 administration (F″ merged). (G–G″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (G) and global acetyl H3 (G′) in the BLA with 10 mg/kg RGFP963 administration (G″ merged). (H–H″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (H) and global acetyl H3 (H′) in the DG with vehicle administration (H″ merged). (I–I″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (I) and global acetyl H3 (I′) in the DG with 10 mg/kg RGFP966 administration (I″ merged). (J–J″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (J) and global acetyl H3 (J′) in the DG with 10 mg/kg RGFP963 administration (J″ merged). (K–K″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (K) and global acetyl H4 (K′) in the BLA with vehicle administration (K″ merged). (L–L″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (L) and global acetyl H4 (L′) in the BLA with 10 mg/kg RGFP966 administration (L″ merged). (M–M″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (M) and global acetyl H4 (M′) in the BLA with 10 mg/kg RGFP963 administration (M″ merged). (N–N″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (N) and global acetyl H4 (N′) in the DG with vehicle administration (N″ merged). (O–O″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (O) and global acetyl H4 (O′) in the DG with 10 mg/kg RGFP966 administration (O″ merged). (P–P″) Photomicrographs showing colocalization of DAPI (P) and global acetyl H4 (P′) in the DG with 10 mg/kg RGFP963 administration (P″ merged).