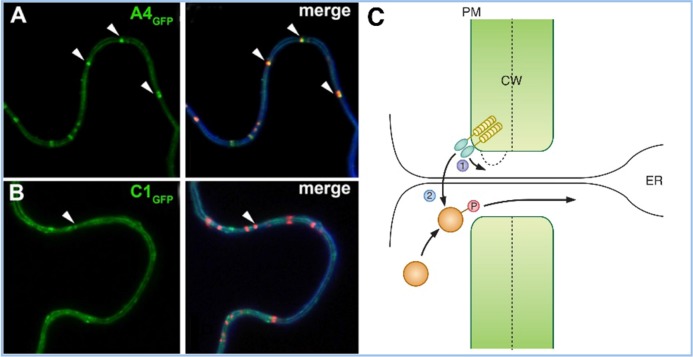
Figure 2. Localization of receptor-like kinases (RLKs) to plasmodesmata (PDs) and their possible consequences.
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusions of ACR4 (A) and CLV1 (CLAVATA1) (B) show plasma membrane and PD-enriched localization (arrow) in the left panels. The right panels show co-localization with a membrane stain, FM4-64 (blue), and aniline blue staining for callose (red). Reproduced with permission from Elsevier [31]. A4, ACR4; C1, CLV1. (C) Two models for the role of RLKs in PD function are proposed: in (1), RLK signaling could control callose deposition and PD permeability; in (2), the RLK could phosphorylate a non-cell autonomous protein, which could allow it to traffic through the PD or restrict its trafficking in the destination cell or do both. Abbreviations: CW, cell wall; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PM, plasma membrane