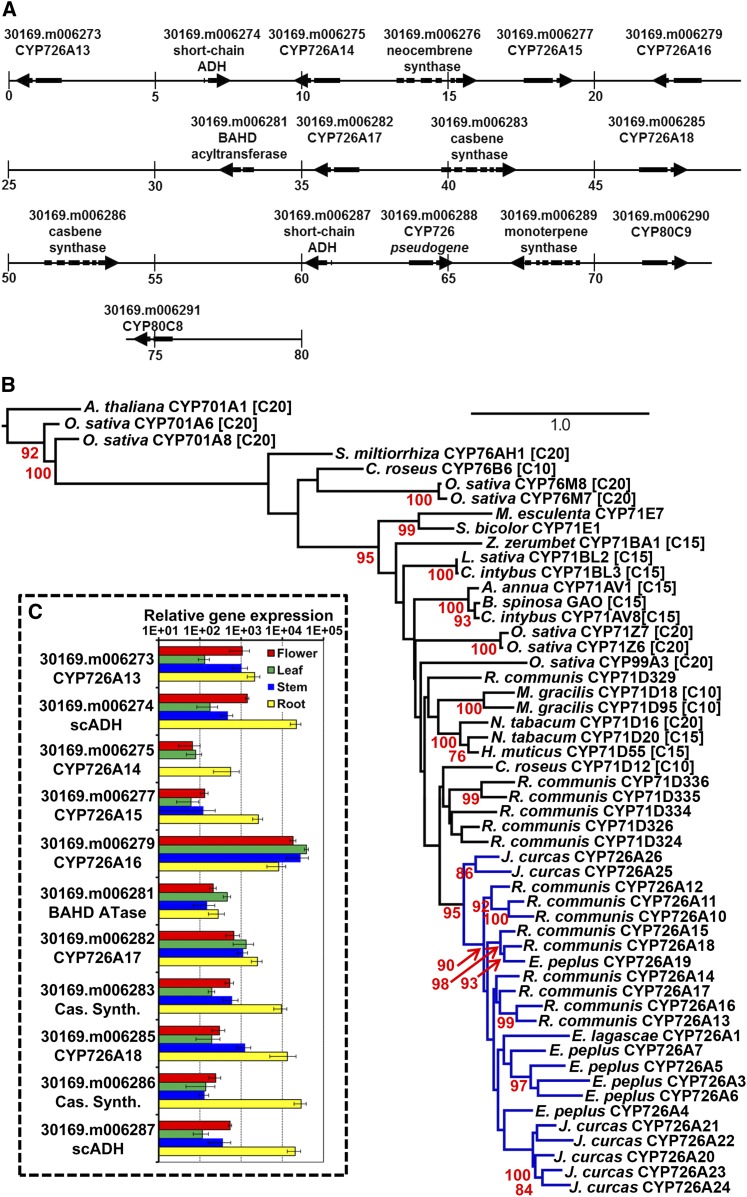
Figure 2.
A Putative Diterpenoid Biosynthetic Gene Cluster from Castor.
(A) An 80-kb section of the R. communis genome containing the proposed diterpenoid biosynthetic gene cluster including genes for diterpene (casbene and neocembrene) synthases, CYP726A proteins, a BAHD acyltransferase, and two short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases. The numbers under the vertical bars represent the position within the gene cluster in kilobases.
(B) Phylogenetic tree obtained for the alignment of peptide sequences of CYP71 clan, including known terpenoid oxidases. Protein sequences are from R. communis CYP726A10 [XP_002532302], CYP726A11 [XP_002532303], CYP726A12 [XP_002532304], CYP71D334 [XP_002523467], CYP71D335 [XP_002514827.1], CYP71D336 [XP_002514826], CYP726A13 [KF986809], CYP726A14 [KF986810], CYP726A15 [KF986811], CYP726A16 [KF986812], CYP726A17 [KF986813], and CYP726A18 [KF986814]); E. lagascae Δ-12 fatty acid epoxidase (CYP726A1 [AAL62063.1]); E. peplus CYP726A3 [KF986822], CYP726A4 [KF986823], CYP726A5 [KF986824], CYP726A6 [KF986825], and CYP726A19 [KF986826]; J. curcas CYP726A20 [KF986815], CYP726A21 [KF986816], CYP726A22 [KF986817], CYP726A23 [KF986818], CYP726A24 [KF986819], CYP726A25 [KF986820], and CYP726A26 [KF986821]; Catharanthus roseus tabersonine-16-hydroxylase (CYP71D12 [ACM92061]) and geraniol-10-hydroxlase (CYP76B6, [Q8VWZ7]; N. tabacum 5-epiaristolochene dihydroxylase (CYP71D20 [Q94FM7]) and α-cembratrienol hydroxylase (CYP71D16 [AAD47832]; Hyoscyamus muticus premnaspirodiene oxidase (CYP71D55 [A6YIH8], Mentha gracilis limonene-6-hydroxylase (CYP71D18 [Q9XHE8] and limonene-3-hydroxylase (CYP71D95 [Q6WKY9]; Zingiber zerumbet α-humulene 10-hydroxlase (CYP71BA1 [E3W9C4]); O. sativa isokaurene C2-hydroxylase (CYP71Z6 [A3A871]), ent-cassadiene C2-hydroxylase (CYP71Z7 [Q6YV88]) ent-cassadiene C11-hydroxylases (CYP76M7 and CYP76M7 [Q69X58 and Q6YTF1] syn-pimaradiene oxidase (CYP99A3 [Q0JF01] and ent-kaurene oxidases (CYP701A6[AAT81230]) and CYP701A8[AAT46567], Lactuca sativa costunolide synthase (CYP71BL2 [F8S1I0]; Cichorium intybus (+)-valencene oxidase (CYP71AV8 [E1B2Z9] and costunolide synthase (CYP71BL3 [G3GBK0]; A. annua amorpha-4,11-diene C-12 oxidase (CYP71AV1 [Q1PS23]; Barnadesia spinosa germacrene A oxidase (BsGAO, D5JBX1.1]; M. esculenta 2-methylbutanal oxime monooxygenase and Sorghum bicolor 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldoxime monooxygenase (CYP71E1 [O48958] and Salvia miltiorrhiza miltiradiene oxidase (CYP76AH1 [AGN04215]), and Arabidopsis ent-kaurene oxidase (CYP701A [NP_197962]). Enzymes known to be involved in mono-, sesqui-, and diterpenoid biosynthesis are indicated by [C10], [C15], and [C20], respectively. CYP726A is highlighted with blue branches. The numbers in red positioned to the left of and below the nodes indicate bootstrap values shown as a percentage based on 1000 replicates. Bootstrap values below 70% are not shown. The scale bar (top right) represents the number of substitutions per site.
(C) Expression of castor diterpenoid genes. Relative transcript levels were calculated against a housekeeping gene (20-kD nuclear cap binding protein) using real-time PCR. For each tissue sample, three biological and four technical replicates were used. The error bars show the standard deviations.