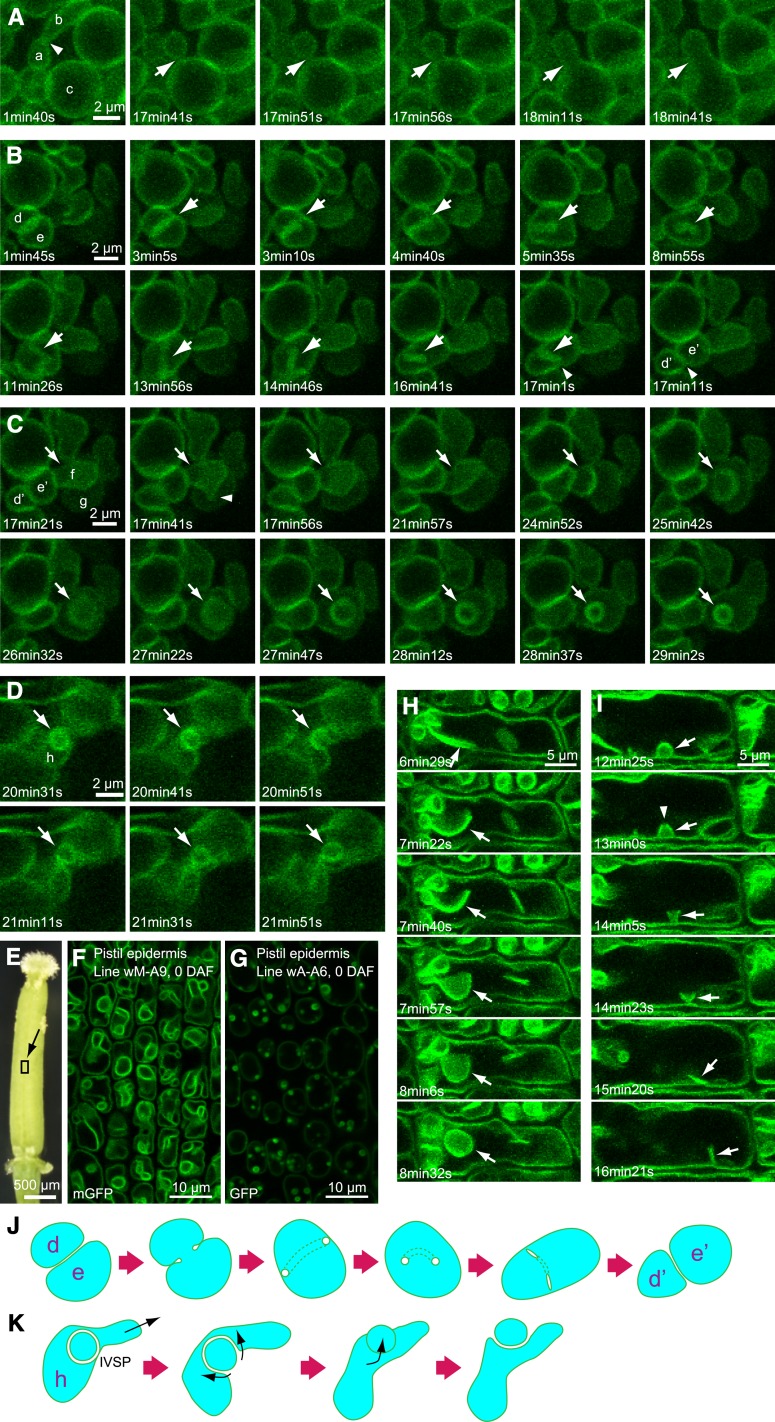
Figure 9.
Vacuolar Dynamics Visualized by VHP1-mGFP.
Peripheral endosperm in a water imbibed seed for 30 h ([A] to [D]) and epidermal cell of the pistil at 0 DAF ([E] and [F]) were observed by XYZT analysis. Figures were constructed by projection of Z-stack images with a 0.47-μm interval. Thickness of observed area: 1.41 μm (four stacks) in (A) to (C), 1.88 μm (five stacks) in (D). All photographs were taken from the wM-A9 line except for (G) (wA-A6).
(A) Vacuolar fusion. Arrows indicate points of vacuole fusion.
(B) Tubular structure (arrows) derived from boundary face between two vacuoles.
(C) IVSP formation by invagination (arrows).
(D) IVSP disappearance. Arrows indicate IVSPs.
(E) 0-DAF pistil.
(F) and (G) Observed area is indicated by square located on the style. Pistil epidermal cell of wM-A9 (F). Pistil epidermal cell of wA-A6 (G).
(H) IVSP formation by sheet folding.
(I) IVSP disappearance. Arrows indicate IVSPs.
(J) Schematic model of dynamic transformation of vacuoles shown in (B).
(K) Schematic model of transformation of an IVSP to a regular small vacuole, as shown in (D).