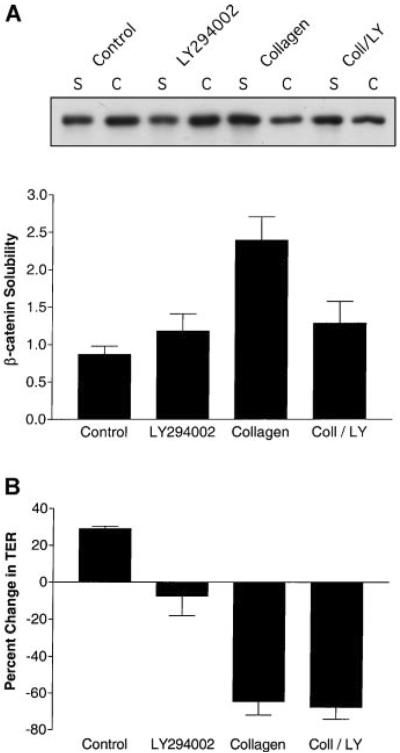
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of PI 3-kinase affected β-catenin association with the cytoskeleton but not tight junction permeability during epithelial remodeling. MDCK cells were incubated for 6 h with DMEM (Control), DMEM containing 20 μM LY-294002, collagen gel overlays (Collagen) or collagen gel overlays containing LY-294002 (Coll/LY; n = 4). A: β-catenin association with the cytoskeleton was determined by differentially detergent solubility, SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. A representative β-catenin immunoblot is presented that includes the TX-100 soluble (s) fractions and the RIPA cytoskeletal (c) extracts. Quantitative data are presented in graph form as the levels of TX-100/RIPA soluble extracts of β-catenin (β-catenin solubility; mean ± SE). Statistical analysis demonstrated that β-catenin ratios for collagen-treated cells (Coll) were significantly different (P < 0.04) from cells incubated in medium alone. B: Tight junction permeability was determined by TER measurements (n = 3). TER (Ω cm2) is presented as % change from initial readings (mean ± SE). The mean starting TER for these experiments was ~150 Ω cm2. When Collagen is compared to the Control there are significant differences (P < 0.01). However, when Collagen/LY-294002 (Coll/LY) is compared to the Control there is no significant difference. This indicates that LY-294002 did not affect collagen-mediated increases in tight junction permeability.