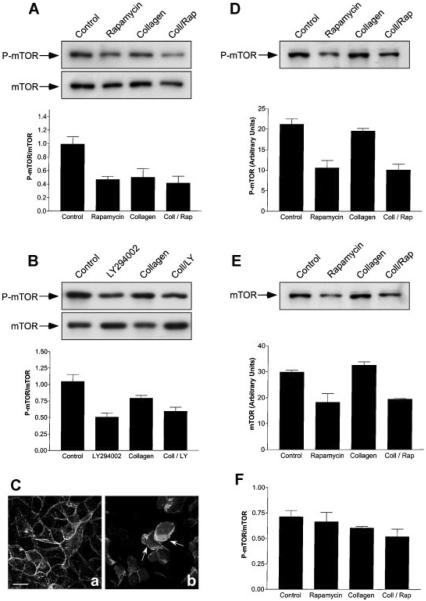
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of mTOR activity during epithelial remodeling. A: MDCK cells were incubated for 6 h with DMEM (Control), DMEM containing 20 nM rapamycin, collagen gel overlays (Collagen), or collagen gel overlays containing rapamycin (Coll/Rap). The cells were detergent-extracted and the levels of total mTOR and activated mTOR (P-mTOR) determined by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting (n = 5). Representative immunoblots are presented. Graphic representation of P-mTOR/mTOR (arbitrary units ± SE) to determine mTOR activation levels demonstrated that Collagen (P < 0.02) and Coll/Rap (P < 0.004) were significantly different from control cells. B: Cells were treated in a manner identical to that described above except that they were incubated for 6 h with, or without, collagen gel overlays containing, or lacking, 20 μM LY-294002. SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting (see representative immunoblots) demonstrated a ~50% inhibition of P-mTOR activity (n = 4; P < 0.002) with collagen gel overlays containing, or lacking, LY-294002. C: Spatial regulation of activated PI3-kinase was not inhibited by rapamycin. MDCK cells stably expressing GFP-Akt-PH were incubated with 20 nM rapamycin or collagen gel overlays containing rapamycin for 6 h. Confocal microscopy demonstrated that GFP-Akt-PH was localized to the basolateral membrane in the presence of rapamycin alone (a). After incubation with collagen geloverlays containing rapamycin, epithelial remodeling occurred as demonstrated by the formation of lamellipodia (b). Under these conditions GFP-Akt-PH was localized to the lamellipodial leading edge (b, arrows). Scale bar, 10 μm. D–F: Long-term incubation with rapamycin induced down-regulation of mTOR. Cells were incubated with DMEM (Control), DMEM containing 20 nM rapamycin, collagen gel overlays (Collagen), or collagen gel overlays containing rapamycin (Coll/Rap) for 24 h (n = 3) and prepared for immunoblotting. D: P-Ser2448-mTOR (P-mTOR) levels (arbitrary units ± SEM). A representative immunoblot demonstrates that treatment with rapamycin or collagen/rapamycin decreased P-mTOR protein levels when compared to the control. Quantitative measurements demonstrated that the level of P-mTOR in Collagen/Rap-treated cells was significantly lower that those in collagen gel alone (P = 0.003). E: Total mTOR levels (arbitrary units ± SE). Treatment with collagen gel did not produce significant decreases in mTOR protein when compared to the control. However, mTOR levels in Collagen/Rap-treated cells were significantly lower that those in control cells (P < 0.005). F: Graphic representation of P-mTOR/mTOR to calculate mTOR activation levels demonstrated that all treatments were not significantly different from control cells.