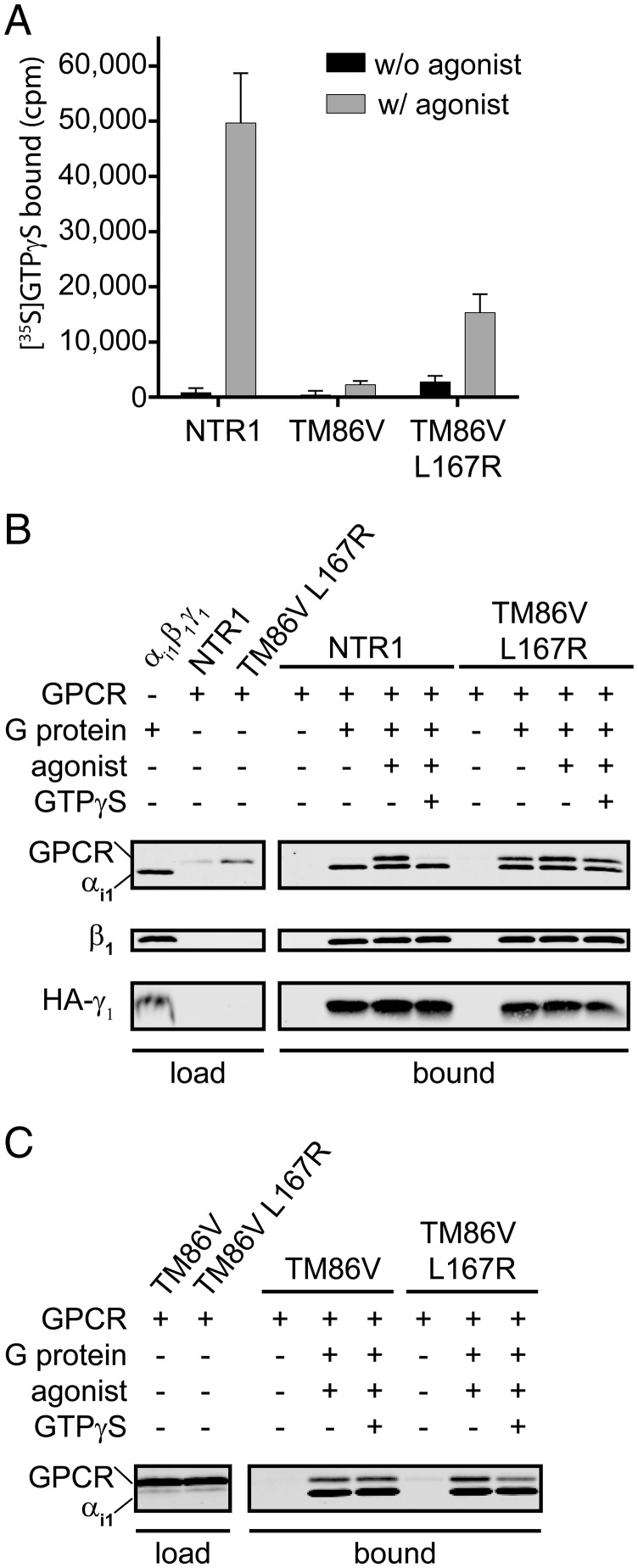
Fig. 2.
Functional interaction of the NTR1 WT receptor and its evolved mutants with G protein. (A) [35S]GTPγS assay of the NTR1 WT receptor, the stabilized mutant TM86V and TM86V with restored E/DRY motif (TM86V L167R). The amount of [35S]GTPγS bound to the G protein (αi1β1γ1) in the presence or absence of the agonist NT (20 µM) is shown. The signals correspond to the average of two or three (NTRI) experiments performed in parallel from independent GPCR expressions. Error bars represent SDs. (B) Results of coimmunoprecipitation experiments of G protein (αi1β1HA-γ1) and NTR1 WT or TM86V L167R. After incubation of the solubilized G protein with anti-HA beads, the beads were incubated with solubilized GPCR. The presence of solubilized proteins before incubation with the beads (load) and the GPCR/G protein bound to the beads as a function of the presence of G protein, ligand (20 µM NT) and GTPγS (750 µM) is shown by Western blot (bound). (C) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments comparing TM86V with TM86V L167R, carried out as described for B.