Figure 2.
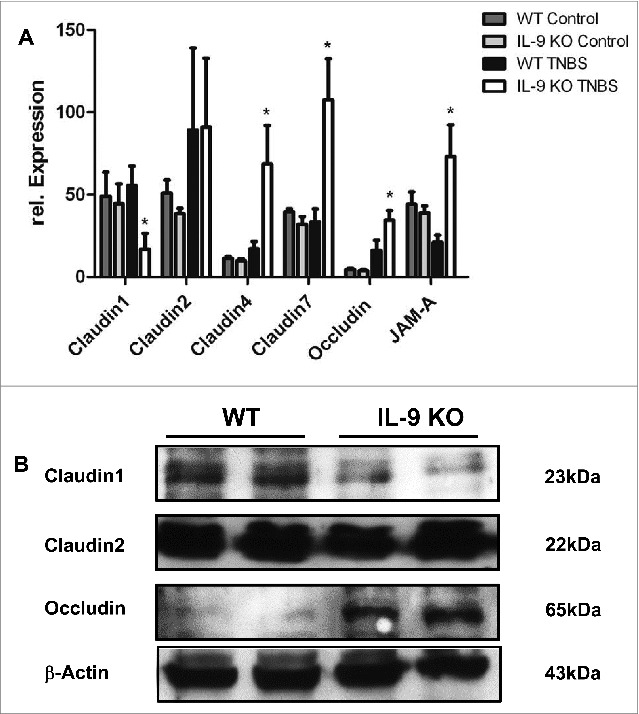
TNBS-induced inflammation led to different expression levels of Claudin1, Claudin4, Claudin7, JAM-A and occludin in WT and IL-9 KO mice. Analysis of tight junction proteins was done in the TNBS-inflamed colon from wild-type and IL-9 deficient animals (A). Total mRNA was isolated from the TNBS inflamed colon and from control WT and IL-9 KO mice and RT PCR quantification was done. Relative expression of Claudin1, Claudin2, Claudin4, Claudin7, JAM-A and occludin was normalized to the house-keeping gene 18sRNA and significant differences were indicated. For statistics 3–9 animals per group were included. Untreated WT and IL-9 KO showed no difference in the expression of all tight junction proteins. Up regulation of Claudin1 mRNA was observed in TNBS-treated WT animals, in contrast to IL- 9 KO mice, whereas Claudin2 levels were unchanged. Claudin4, Claudin7 and JAM-A mRNA expression was significantly down regulated in inflamed WT mice. Occludin mRNA was downregulated in TNBS-inflamed WT mice in comparison to IL-9 deficient mice. Western Blot quantification of tight junction proteins was done in protein extract from isolated epithelial cells from TNBS treated WT and IL-9 KO animals (B). Each lane contained proteins from 0.25 x 106 epithelial cells. Protein bands of β-actin served as loading control. Claudin1 showed more protein in epithelial cells from TNBS inflamed WT mice, contrarily, occludin levels were lower. Protein levels of Claudin2 were unchanged in both groups. Western Blot analysis was done with 4 mice per group. A representative set of 2 animals per group are shown.
