Figure 3.
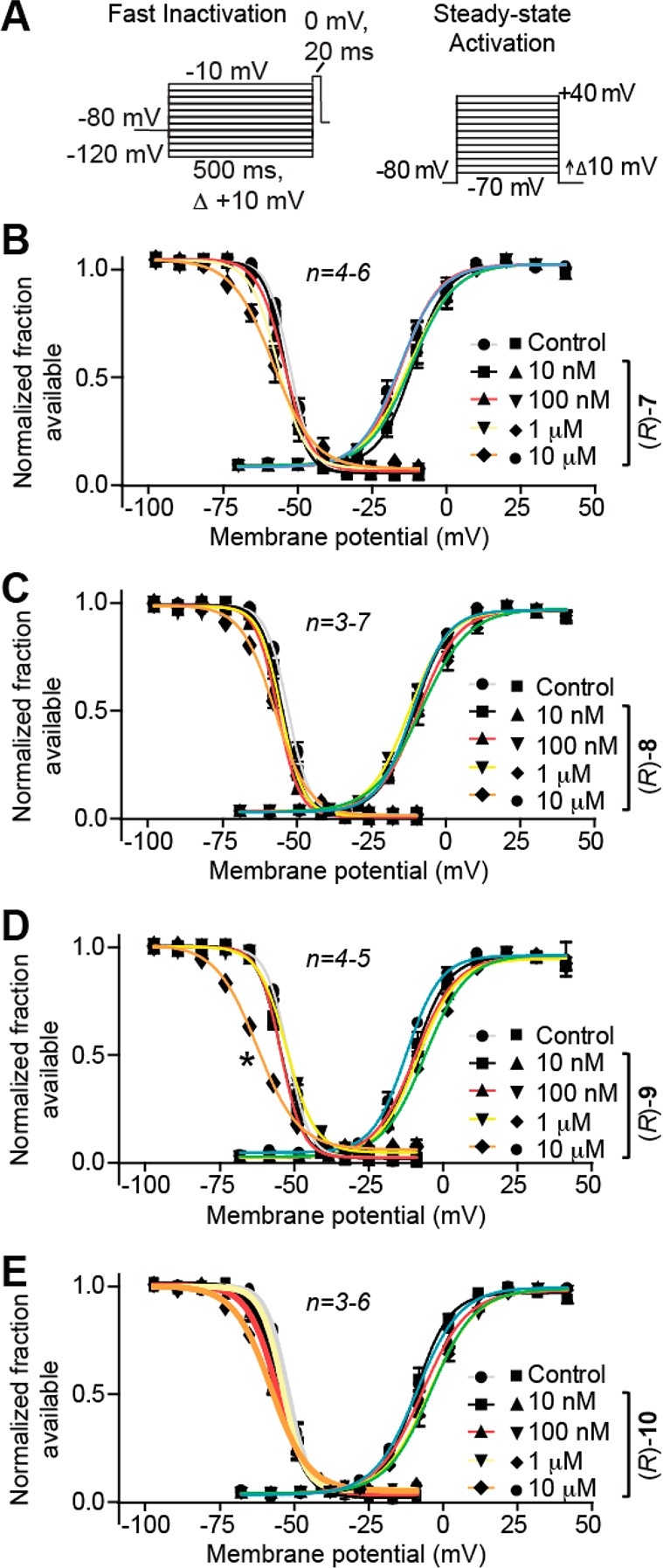
Effects of the chimeric compounds (R)-7–(R)-10 on fast inactivation and steady-state activation states of Na+ currents in CAD cells. (A) Fast inactivation (left) and steady-state activation (right) voltage protocols. (B–E) Representative Boltzmann fits for steady-state fast inactivation and steady-state activation for currents recorded from CAD cells treated with 0.1% DMSO (control) and various concentrations of the indicated compounds are graphed. Values for V1/2, the voltage of half-maximal inactivation and activation, and the slope factors (k) were derived from Boltzmann distribution fits to the individual recordings and averaged to determine the mean (±SEM) voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation and activation, respectively. The V1/2 value of cells treated with 10 μM (R)-9 of −76.5 ± 0.6 (n = 5) was signigifantly greater than that of control (0.1% DMSO) cells (−63.8 ± 0.4 (n = 4); p < 0.05, Student’s t test). The V1/2 and k of steady-state fast inactivation or steady-state fast activation were not different among any of the other compounds tested (p > 0.05, one-way ANOVA). Data from n = 3–7 cells per condition.
