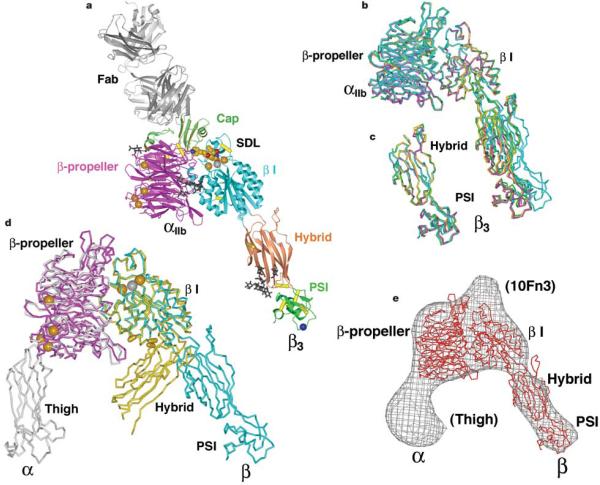
Figure 2.
Structure of the αIIbβ3 headpiece. a, Ribbon diagram of the αIIbβ3:10E5 complex. Calcium and magnesium ions are shown as gold and silver spheres, respectively. Tirofiban is shown in cpk. The Cα atom of HPA-1a alloantigenic determinant Leu 33 in the PSI domain is shown as a blue sphere. Glycan chains are displayed as black sticks. Integrin disulphides are shown as yellow Cα –Ca bonds. b, Superimposed on the basis of the β I domain are the three independent αIIbβ3 heterodimers in crystal form B (magenta, green and yellow), and one in form A (cyan). c, The hybrid and PSI domains of the four independent αIIbβ3 structures are superimposed. d, Liganded-open αIIbβ3 (crystal form A) and unliganded-closeda αVβ3 headpieces7 are superimposed using the β I domainb -sheet. The α and β subunits are coloured magenta and cyan in αIIbβ3 and grey and yellow in αVβ3. Calcium and magnesium ions inαIIbβ3 only are gold and silver spheres, respectively. Yellow cylinders in the β I/hybrid interface show positions of residues where introduction of N-glycosylation sites induces high affinity for ligand and LIBS epitope exposure9,42. e, Superposition of an αIIbβ3 structure from crystal form B (red Cα-trace) on the three-dimensional electron microscopy density (grey chickenwire) of the fibronectin-bounda β5β1 headpiece6. Domains are labelled and those only in the α5b1 structure including the tenth FN3 domain of fibronectin are in parentheses. Figures in this paper utilize crystal form A unless stated otherwise and were prepared with programs Bobscript46, Povray (The Povray Team, http://www.povray.org), Raster3D47 and Ribbons48.