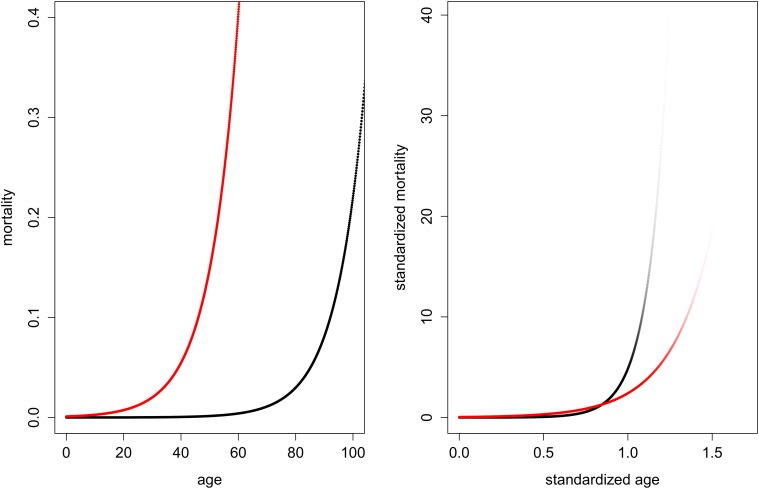
Fig 2. The effect of pace standardization on age-specific hazard can reverse conclusions.
Gompertz mortality μ(x) = ae 0.1x with a = 0.00001 (black line) and a = 0.001 (red line). Left: unstandardized perspective. Right: standardized perspective. The intensity of the colors is proportional to the value of the respective survival function. If the strength of aging is measured by how steeply age-specific hazard increases over life, the unstandardized perspective implies that the population with a = 10−3 experiences stronger aging than the population with a = 10−5; however, if the difference in life span is accounted for, i.e., if the hazard curves are standardized, the conclusion is reversed.