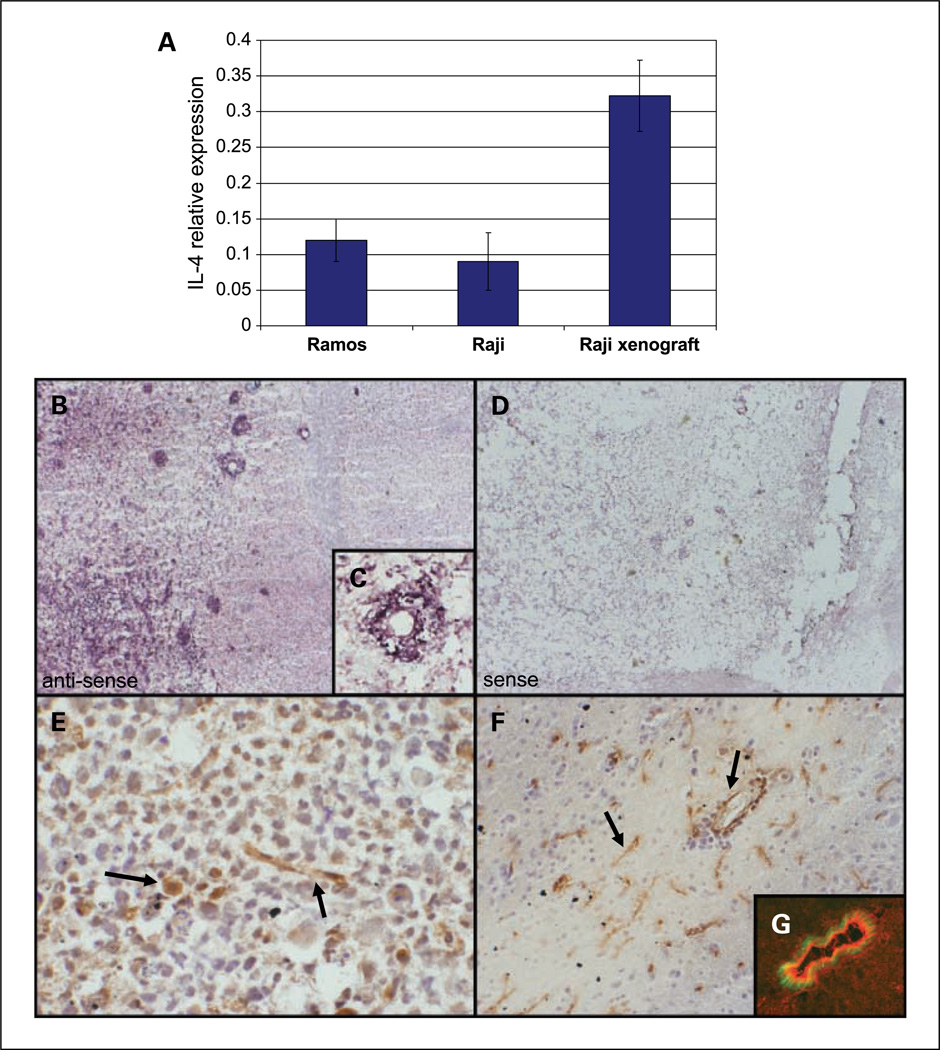
Fig. 2.
IL-4 expression by lymphoma cells in culture and CNS lymphoma xenograft. A, quantitative RT-PCR using human-specific IL-4 primers shows constitutive IL-4 expression by Raji and Ramos lymphoma cell lines in culture (normalized to GUS expression). Intracranial implantation of Raji lymphoma cells resulted in a >3-fold increase in relative IL-4 expression (P < 0.03). To confirm the species specificity of the primers used, we showed that human IL-4 RNA could not be detected by quantitative RT-PCR using RNA derived from spleen or brain of mice not implanted with intracranial lymphoma cells (data not shown). B, in situ hybridization with an antisense riboprobe against IL-4 shows intratumoral expression in a xenograft model of CNS lymphoma both by tumor cells and by vascular endothelia (×200). There was no evidence for IL-4 expression in normal mouse brain. C, higher magnification of a tumor vessel (×400). D, a sense riboprobe against IL-4 resulted in no significant hybridization in a parallel section from the same tumor (×200). E, expression of IL-4 by tumor macrophage (large arrow) and blood vessel (small arrow; ×200). F, IL-4 expression by microvessels in the periphery of the lymphoma (×100). G, dual-color immunofluorescence shows colocalization of IL-4 (red) and VWF (green) in parallel section of experimental CNS lymphoma model (×400).