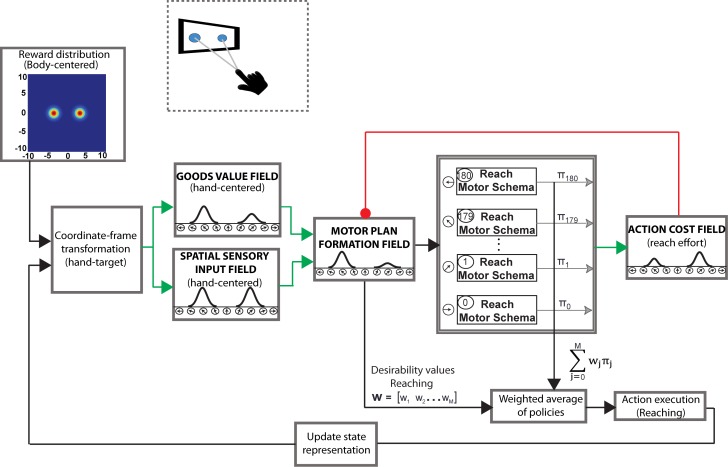
Fig 2. A simplified version of the model architecture for reaching decision tasks in the presence of two competing targets.
The motor plan formation field encodes the direction of the intended arm movement in a special reference frame centered on the hand. The goods-based decision values and the spatial sensory inputs are therefore transformed from allocentric to egocentric representations centered on the hand before being input to the motor plan formation field. The motor plan formation field integrates information about the spatial location of the targets, the expected reward attached to each target and the action cost required to pursue the targets into a single variable named “relative desirability”. The relative desirability encodes the “attractiveness” of the individual M reach policies at a given time and state and is used to weigh the influence of these policies on the final policy. Note that M is the number of neurons with activation level above a threshold γ. Once the final policy is determined, the framework implements that policy at the given time and state resulting in an action-plan (i.e., sequences of actions) that drives the hand closer to the target (see Results and Methods sections for more details).