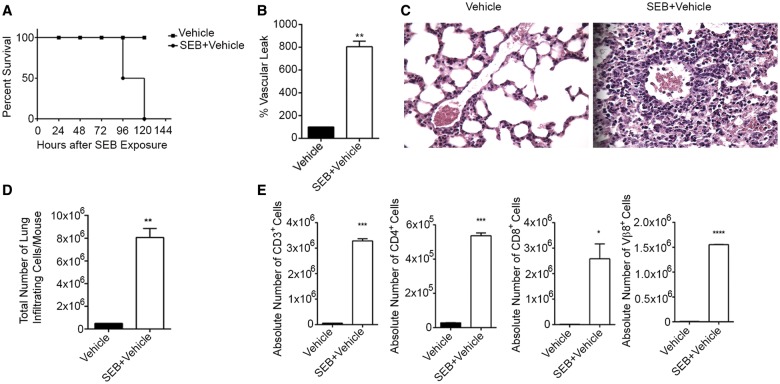
FIG. 1.
SEB exposure results in pulmonary inflammation and mortality of mice. C3H/HeJ mice were exposed to a “Dual Hit” of SEB and euthanized 72 h post-exposure. A, Survival curve of mice exposed to either vehicle or SEB. B, Measurement of vascular leak 24 h after exposure to the second dose of SEB. Mice were administered Evans Blue dye and following perfusion, lungs were placed in formamide. Absorbance was recorded at 620 nm and the percentage of vascular leak was calculated and graphically represented. C, Representative H&E (×40) staining of sections of the lung demonstrating immune cell infiltration. D, Total number of mononuclear cells infiltrating the lungs in vehicle or SEB exposed mice as determined by trypan blue exclusion method. E, Phenotypic characterization of mononuclear cells infiltrating the lung determined by staining cells with fluorescein-conjugated antibodies against CD4, CD8, and Vβ8 and conducting flow cytometric analysis. Absolute cell counts are represented graphically. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 5) from 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance is indicated as follows: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 (when compared with vehicle).